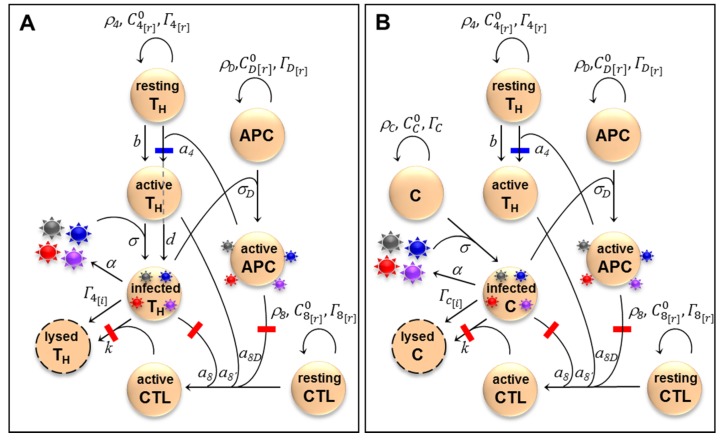
Figure 3. Schematic representation of the HIV immune activation model and the control model.
(A) Model of the cellular immune response against HIV. In the absence of immune activation, pools of resting TH (CD4) cells, CTLs (CD8), and pAPCs divide at rates, ρ4, ρ8, ρD and die at rates 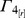 ,
, 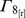 , and
, and 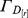 , reaching homeostatic concentrations
, reaching homeostatic concentrations 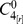 ,
, 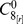 , and
, and 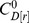 , respectively. Activated TH cells become infected through contact with free virions at a rate constant σ, whereas resting cells are assumed to be non-susceptible to the virus. TH cells are activated at a rate constant a4 after contacting a pAPC with an HIV epitope or by other antigens at rate constant b (background activation). TH cells establishing synapses with pAPCs have a probability d of being concomitantly infected with the same viral type. Infected cells release virions at a rate constant α and die at a rate constant
, respectively. Activated TH cells become infected through contact with free virions at a rate constant σ, whereas resting cells are assumed to be non-susceptible to the virus. TH cells are activated at a rate constant a4 after contacting a pAPC with an HIV epitope or by other antigens at rate constant b (background activation). TH cells establishing synapses with pAPCs have a probability d of being concomitantly infected with the same viral type. Infected cells release virions at a rate constant α and die at a rate constant 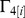 . CTL pre-activation occurs after contacting infected cells (a8) or pAPCs (a8D). A co-stimulatory signal from activated TH cells is necessary for completing CTL activation (a8′). Infected cells are lysed by CTLs at a rate constant k. Death rate constants for activated TH cells
. CTL pre-activation occurs after contacting infected cells (a8) or pAPCs (a8D). A co-stimulatory signal from activated TH cells is necessary for completing CTL activation (a8′). Infected cells are lysed by CTLs at a rate constant k. Death rate constants for activated TH cells 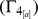 , CTLs
, CTLs 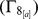 , and pAPCs
, and pAPCs 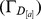 and virion inactivation rates (ΓV) are not shown for simplicity. The full list of variables and parameters is available in Appendix S1, which also provides references to empirical work justifying the parameter values used (see also main text). A fraction μ of the virions released in each cell infection become escape mutants. Avoidance of CTL activation or CTL-mediated killing leads to CTL escape (red bars), whereas avoidance of TH cell activation leads to TH escape (blue bars). The model allows full T-cell (purple), TH-only (blue), and CTL-only (red) escape mutants. (B) Control model in which the virus targets a nonimmune cell type C (e.g., hepatocytes, epithelial cells, etc.) instead of TH cells. Two key differences with the HIV model are that viral replication is not dependent upon immune activation and that transinfection does not take place. Variables, parameters, and equations for this model are also shown in Appendix S1.
and virion inactivation rates (ΓV) are not shown for simplicity. The full list of variables and parameters is available in Appendix S1, which also provides references to empirical work justifying the parameter values used (see also main text). A fraction μ of the virions released in each cell infection become escape mutants. Avoidance of CTL activation or CTL-mediated killing leads to CTL escape (red bars), whereas avoidance of TH cell activation leads to TH escape (blue bars). The model allows full T-cell (purple), TH-only (blue), and CTL-only (red) escape mutants. (B) Control model in which the virus targets a nonimmune cell type C (e.g., hepatocytes, epithelial cells, etc.) instead of TH cells. Two key differences with the HIV model are that viral replication is not dependent upon immune activation and that transinfection does not take place. Variables, parameters, and equations for this model are also shown in Appendix S1.