Figure 2.
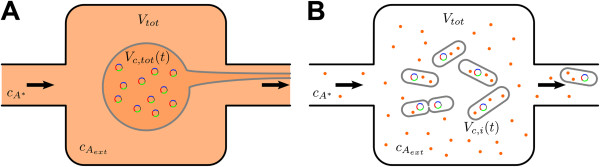
Scheme of the deterministic and stochastic modelling approaches. A: In the deterministic model, the population of cells is described by a unique volume with average and continuous concentrations of all species, including the DNA carrying the QS network (small circles). Cellular growth is also taken into account in this approach. B: In the stochastic model, cells are modelled as individual compartments that can grow and divide and all molecular species are represented as discrete entities. In both cases, A and B, we assume that all species are well-stirred inside the cells and in the medium. In order to maintain a constant cell density, as in the experiments we aim to model, we implement a dilution protocol. In the deterministic model the dilution removes continuously cytoplasmic material in order to compensate the cell growth. In the stochastic model individual cells are removed every time a new cell is born (see Additional file 2: Video S1).
