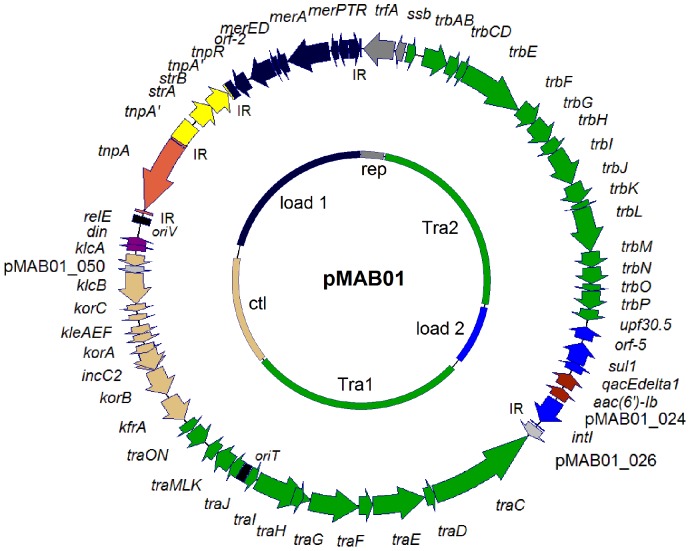
Figure 1. Genetic map of the IncP-1β plasmid pMAB01.
The coding regions are indicated with arrows showing the direction of transcription. The inverted repeats (IRs) of the transposons and integrons are identified. The origins of vegetative replication (oriV) and plasmid transfer (oriT) are indicated with black boxes. The functional modules of the plasmid backbone are differentiated by colors in the inner circle: Tra1 (tra) and Tra2 (trb) (green); replication (rep) module (trfA-ssb) (grey); central control (ctl) region encoding regulatory and stability functions (kfrA – relE) (light brown). One genetic load region (load 1) contains the following: a Tn501-like mercury-resistance (mer) transposon (dark blue); a truncated Tn5393c streptomycin-resistance transposon (yellow); and a copy of the insertion element IS1071 (orange). The second genetic load region (load 2) contains a class 1 integron with an integrase (intI) and the integron-specific segment qacEdelta1-sul1-orf5 (light blue), with two cassettes, encoding an aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase (aac(6’)-Ib) and a glyoxalase-like domain protein (pMAB01-024) (brown). A detailed description of the accessory regions is shown in Figure 2.