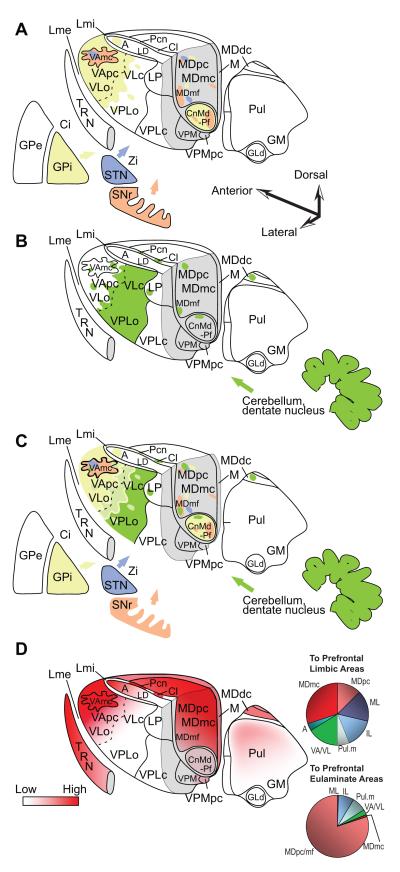
Figure 4.
Innervation of the primate thalamus from the basal ganglia, cerebellum, and connections with prefrontal cortices, based on pathway studies in non-human primates [e.g. (Francois, Tande, Yelnik, & Hirsch, 2002; Sidibe, Pare, & Smith, 2002; Rouiller, Liang, Babalian, Moret, & Wiesendanger, 1994; Sakai, Inase, & Tanji, 1996; Sakai, Stepniewska, Qi, & Kaas, 2000; Erickson, Melchitzky, & Lewis, 2004)]. A, Matched coloring shows projections from the output nuclei of the basal ganglia. B, Shows projections from the output of the cerebellum through the dentate nucleus. C, Overlap of A and B. D (left), Prefrontal connections with the thalamus. D (right), Relative distribution of thalamic projection neurons directed to cingulate and orbital limbic areas (top, limbic) and to the eulaminate areas 46, 8 and 9 (bottom). Quantitative data are from: (Barbas, Henion, & Dermon, 1991; Dermon & Barbas, 1994). Abbreviations: A, anterior nuclei; Ci, internal capsule; Cl, centrolateral nucleus; CnMd, centromedian nucleus; GLd, lateral dorsal nucleus geniculate; GM, medial nucleus geniculate; GPe, globus pallidus external; GPi, globus pallidus internal; LD, lateral dorsal nucleus; Lme, external lamina; Lmi, internal lamina; LP, lateral posterior nucleus; M, midline nuclei; MDdc/mc/mf/pc, the densocellular (dc), magnocellular (mc), multiform (mf), and parvicellular (pc) subdivisions of the mediodorsal (MD) nucleus; Pcn, paracentral nucleus; Pul, pulvinar nucleus; TRN, thalamic reticular nucleus; SNr, substantia nigra reticulata; STN, subthalamic nucleus; VAmc/pc, magnocellular (mc) and parvocellular (pc) subdivision of the ventral anterior (VA) nucleus; VL, ventrolateral nucleus; VLc, caudal ventrolateral nucleus; VLo, oral ventrolateral nucleus; VPLc, caudal subdivision of the ventral posterior-lateral nucleus; VPLo, oral subdivision of the ventral posterior-lateral nucleus;VPM, medial ventroposterior nucleus; VPMpc, parvocellular subdivision of the medial ventroposterior nucleus; Zi, zona incerta.