Table 2. The empirical networks we study and their basic properties.
| N | M | k | κ | ℓ | C | r | |
| Social network of frequent associations between dolphins [36] | 62 | 159 | 5.13 | 1 | 3.357 | 0.258 | −0.043 |
| Coauthorships between scientists posting preprints on the High-Energy TheoryE-Print Archive [37] | 8361 | 15751 | 3.77 | 1332 | 7.025 | 0.442 | 0.294 |
| Coauthorship network of scientists working on network theory and experiment [38] | 1589 | 2742 | 3.45 | 396 | 5.823 | 0.637 | 0.462 |
| Network representing the topology of the Western States Power Grid of the United States [1] | 4941 | 6594 | 2.67 | 1 | 18.989 | 0.080 | 0.003 |
| Neural network of the worm C. elegans [1], [34] | 297 | 2148 | 14.465 | 1 | 2.455 | 0.292 | −0.163 |
| Network of protein-protein interactions in the yeast S. cerevisiae [35] | 2361 | 7182 | 6.084 | 101 | 4.376 | 0.130 | −0.085 |
Number of vertices 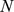 , number of edges
, number of edges 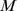 , average degree
, average degree 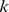 , number of connected components
, number of connected components  , average path length
, average path length 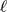 , clustering coefficient
, clustering coefficient  , and coefficient of assortativity
, and coefficient of assortativity  .
.
