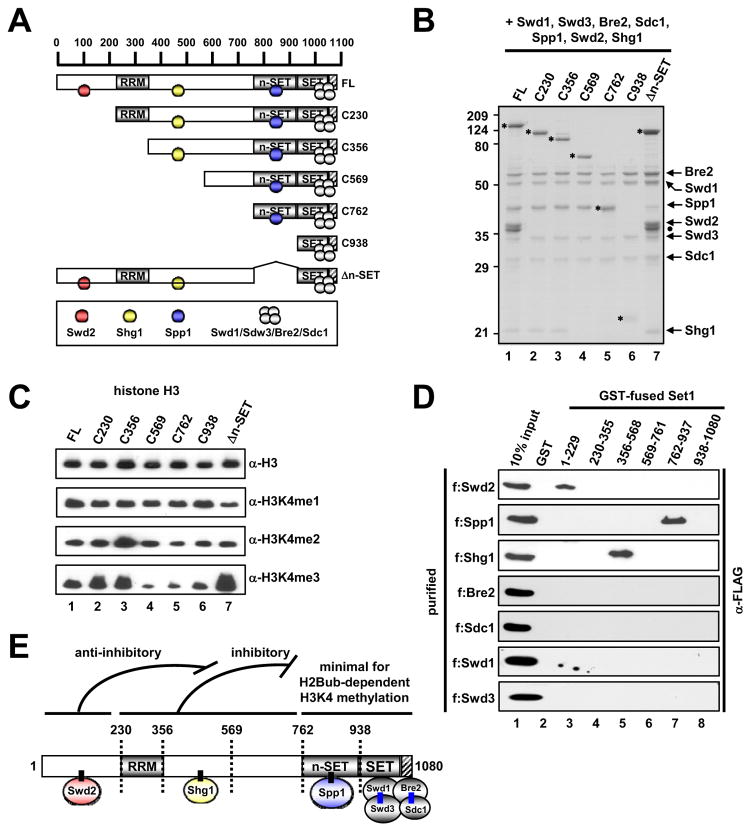
Figure 3. Subunit Interactions within the Yeast Set1 Complex.
(A) A schematic diagram of Set1 and derived fragments, with predicted RRM, n-SET, SET and post-SET domains, and subunit associations deduced from interaction studies. Hatched box, the post-SET domain in this and other figures.
(B) SDS-PAGE/Coomassie Blue staining of purified ySet1Cs reconstituted with baculoviruses expressing FLAG-Set1 or FLAG-Set1 fragments and all seven (untagged) ySet1C subunits. FLAG-Set1 polypeptides are marked by asterisks. Complex loading was normalized to Swd1, Swd3, Bre2 and Sdc1. Note that the C762 Set1 fragment co-migrates with Spp1.
(C) In vitro HMT assays with free histone H3 and indicated purified ySet1Cs.
(D) Direct binding of purified FLAG-tagged ySet1C subunits (Figure S3G) to GST-Set1 fragments (Figure S3F) relative to GST.
(E) Schematic model of subunit interactions with Set1. Direct interactions established in this study are depicted by short, black connecting lines. Direct Bre2-Sdc1 and Swd1-Swd3 interactions established in earlier studies (Roguev et al., 2001; Dehé et al., 2006; Halbach et al., 2009) are indicated by blue lines. Apparent functions of Set1 domains in methylation activity, indicated at the top, are deduced from Figure 4. Numbers indicate amino acid residues. Although not depicted, an interaction between Swd1-Swd3 and a region that lies N-terminal to the SET domain (probably the n-SET domain associated with Spp1: see Figure 6) is suggested by the observation that a Set1 fragment encoding residues 1–900 is co-immunoprecipitated with Swd1-Swd3 (Dehé et al., 2006).
See also Figure S3.