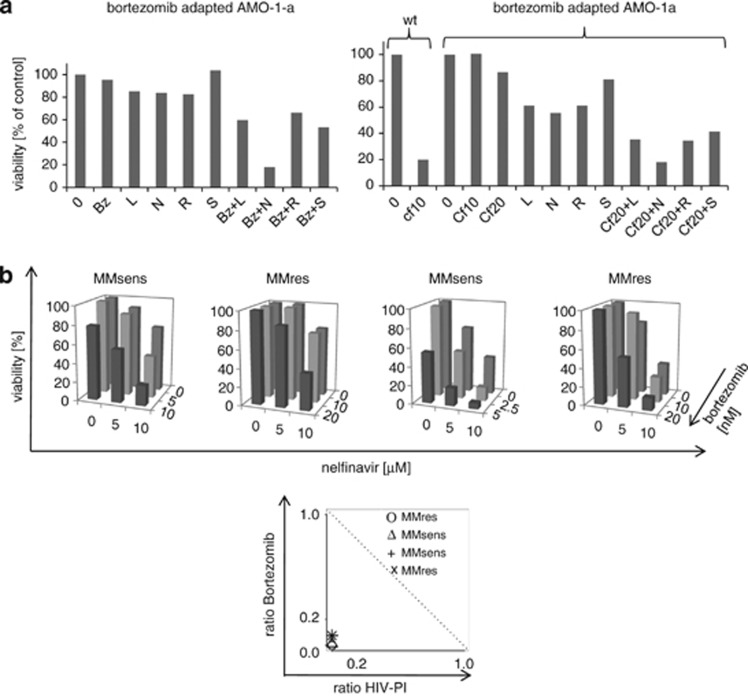
Figure 6.
Synergistic activity of nelfinavir and bortezomib on bortezomib/carfilzomib-resistant myeloma cells. (a) right panel: Bortezomib-resistant AMO-1a cells were coincubated with bortezomib (Bz) 20 nℳ and the HIV-PI indicated (L. lopinavir; N: nelfinavir; R: ritonavir; S: saquinavir, 20 μℳ each) alone or in combination, and cytotoxicity was measured. Right panel: AMO-1 or AMO-1a cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of carfilzomib (Cf, 10=10 nM, 20=20 nℳ) alone or in combination with nelfinavir (N), ritonavir (R), lopinavir (L) or saquinavir (S) (20 μℳ each) and the proportion of viable cells was assessed by dimethylthiazol-diphenyltetrazole test. (b) Upper panel: primary cell samples from bortezomib-resistant or -sensitive myeloma cell samples (MMsens, MMres) were coincubated with increasing concentrations of nelfinavir (0-10 μℳ) in combination with increasing concentrations of bortezomib (0- up to 20 nℳ, as indicated), and cell viability was assessed. Lower panel: The synergistic cytotoxic effect of nelfinavir and bortezomib on bortezomib-resistant primary myeloma cell samples is statistically confirmed by Isolobograms (symbols below the dashed line statistically indicate synergism).