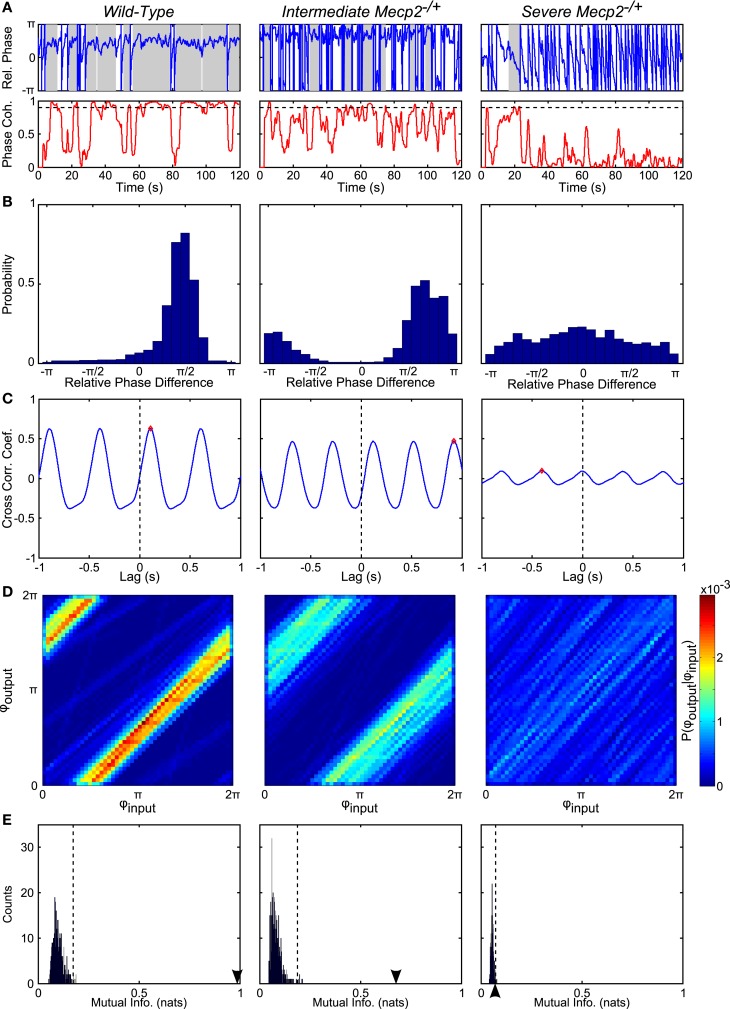
Figure 4.
Representative analyses show reduced phase-locking in Mecp2−/+ compared to wild-type mice. (A) From the instantaneous phase time series, φoutput and φinput, we computed the relative instantaneous phase difference time series, φoutput − φinput (top panels). Regions with near zero slope are indicative of input-output entrainment, which was more frequently observed in wild-type relative to Mecp2−/+ mice. Phase coherence (bottom panels) is a windowed measure that captures the strength of input-output entrainment. A threshold of 0.9 (dashed line in bottom panels) was used to determine windows with significant input-output phase-locking (shaded regions in top panels). Mecp2−/+ mice had increased latency to and reduced duration of entrainment relative to wild-type mice. (B) Representative histograms of the instantaneous phase difference are shown for a wild-type (left panel) and Mecp2−/+ mice (middle and right panels). In all cases, even the severe Mecp2−/+ mice, the distribution was significantly different from a uniform circular distribution as determined by the Rayleigh test for circular non-uniformity. (C) Representative cross-correlograms are shown for a wild-type (left panel), intermediate Mecp2−/+ (middle panel), and severe Mecp2−/+ (right panel) mice. The maximum of the cross-correlogram was reduced in Mecp2−/+ versus wild-type mice. (D) Representative joint probability histograms of the instantaneous input- and output-phases depict the strength of input-output entrainment in the intensity of banding. Entrainment was strong in wild-type and intermediate Mecp2−/+ preparations, but was abolished in severe Mecp2−/+ mice. (E) The significance of the observed input-output entrainment was determined by generating bootstrap distributions of the mutual information of the instantaneous phases. Surrogate instantaneous phase time series were generated by shuffling the input- and output-inter-event intervals before determining the phase. The observed value of the mutual information is indicated by the arrowheads on the abscissa. The upper-bound of the 99% confidence interval is indicated by dashed vertical lines. Wild-type and intermediate Mecp2−/+ mice always showed significant input-output entrainment, whereas severe Mecp2−/+ mice did not have significant input-output entrainment.