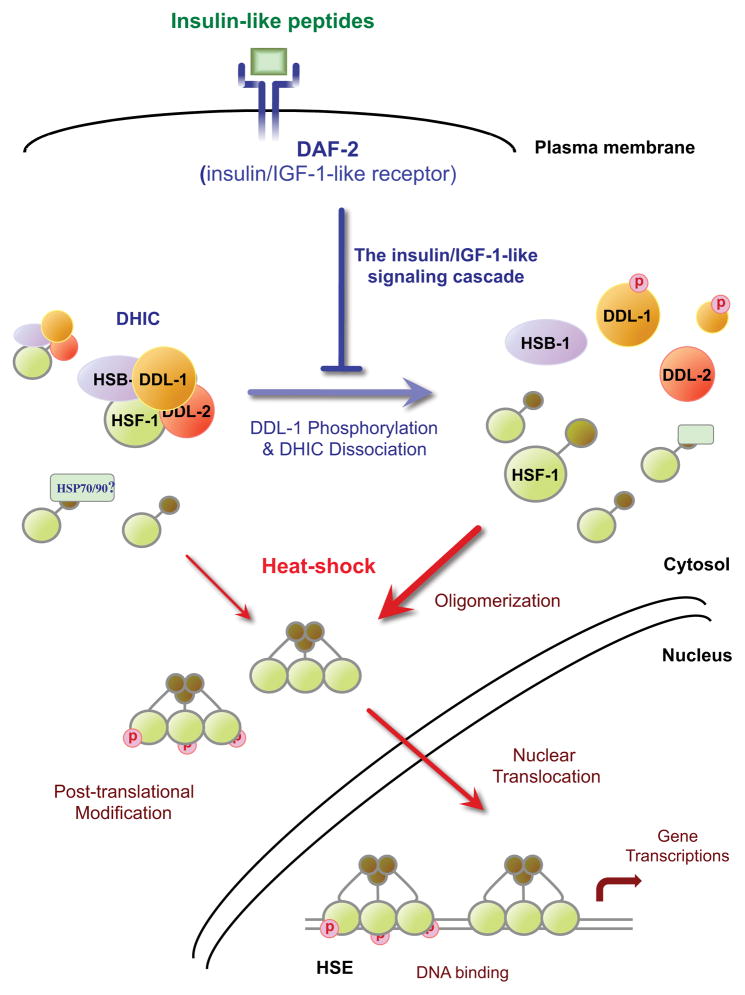
Figure 6. Model of HSF-1 activation regulated by IIS in C. elegans.
Upon heat stress stimulation, HSF-1 undergoes oligomerization, post-translational modification, and nuclear translocation in an undefined order before acquiring DNA-binding and transcriptional activity. The formation of a DDL-1 containing HSF-1 inhibitory complex (DHIC), consisting of HSF-1, HSB-1, DDL-1 and DDL-2, reduces the pool of HSF-1 susceptible to heat stress stimulation. Increased insulin/IGF-1-like signaling (IIS) promotes the formation of DHIC, while reducing DAF-2 activity promotes DDL-1 phosphorylation and disrupts DHIC formation and consequently increases HSF-1 activity under both stressed and unstressed conditions.