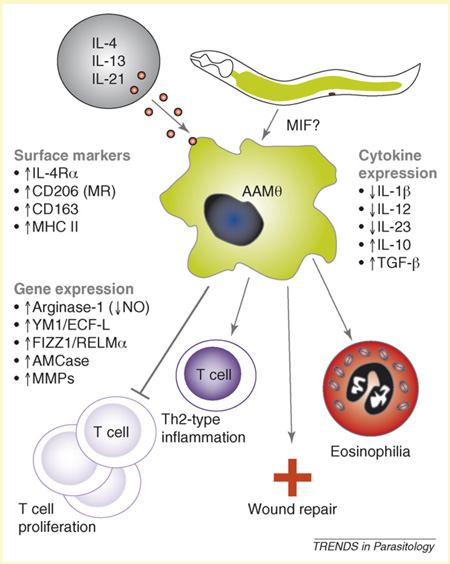
Figure I.
Illustration of alternative activation of macrophages and potential mechanism for parasitic nematode-derived, MIF-induced production of AAMΦs [23]. Alternative activation of macrophages is mediated by interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-13 and possibly IL-21 acting through surface receptors. Characteristic features of AAMΦs include: upregulation of surface receptors including IL-4 receptor (IL-4R), CD-206 (mannose receptor), CD163 (group B scavenger receptor), and MHC II (major histocompatibility class II), among others [54,60]; increased transcription of arginase-1, Ym1/ECF-L (eosinophil chemotactic factor-L), FIZZ1/RELMα (found in inflammatory zone/resistin-like molecule), AMCase (acidic mammalian chitinase) and MMPs (matrix metalloproteinases), among others [53]; modulated expression of cytokines IL-1β, IL-12, IL-10 and transforming growth factor (TGF)- β [4,54]; suppression of T-cell proliferation Th2-type inflammation; and wound repair and eosinophilia [61].