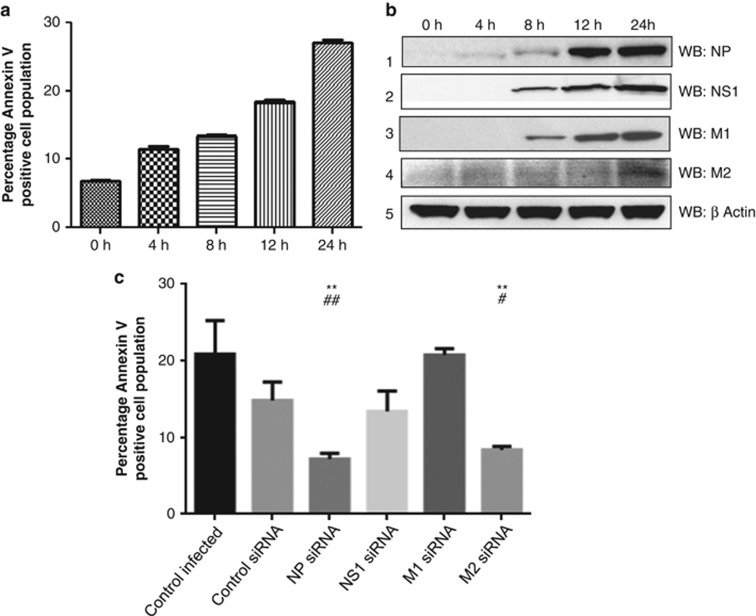
Figure 1.
IAV NP contributes to IAV-induced host cell death. (a) A549 cells were infected with A/California/08/2009(H1N1) IAV at an multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.2. Cells were harvested at different time intervals, stained with Annexin V PE and subjected to flow cytometry. The percentage of Annexin V-positive cell population is plotted on the graph, which shows means±S.D. from one representative experiment (n=3) of at least three independent experiments. (b) From the above mentioned time points, cell lysates were subjected to western blotting using antibodies against NP (rabbit polyclonal: ab 22285), NS1, M1, M2 and β-actin proteins shown in panels 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5, respectively. (c) A549 cells were transfected with siRNA pool against NP, NS1, M1, M2 gene of A/California/2009(IAV) IAV or control nontargeting siRNA. Six hours post-transfection, cells were infected with respective IAV at 0.2 MOI. Cells 12 h postinfection, stained with Annexin V PE and subjected to flow cytometry. The percentage of Annexin V-positive cell population was plotted on the graph. Data show mean±S.D. from one representative experiment (n=3) of at least three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined using Student's t-test. *, #P<0.05; **, ##P<0.01, * and # indicate P values compared to control infected and control siRNA samples respectively