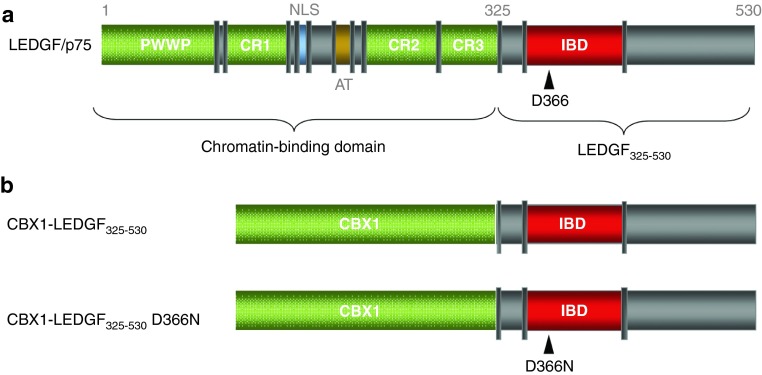
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the LEDGF/p75 domain structure and of the CBX1-LEDGF325-530 fusion. (a) LEDGF/p75 carries a conserved PWWP-domain and several charged regions (CR) at its N-terminus. Together with the nuclear localization signal (NLS) and the AT hook-like domains (AT), these elements form the DNA-binding domain of LEDGF/p75. The C-terminal IBD domain is responsible for the interaction with HIV-IN. D366 is essential for the interaction with HIV-IN (indicated by an arrowhead): mutation of this residue to Asn (D366N) results in loss of interaction. (b) The CBX1-LEDGF325-530 and CBX1-LEDGF325-530 D366N fusions are depicted. All protein elements are drawn to scale. Numbers indicate amino acids. CBX1, heterochromatin protein 1β IBD, integrase-binding domain; IN, integrase; LEDGF/p75, lens epithelium-derived growth factor; PWWP, Pro-Trp-Trp-Pro domain.