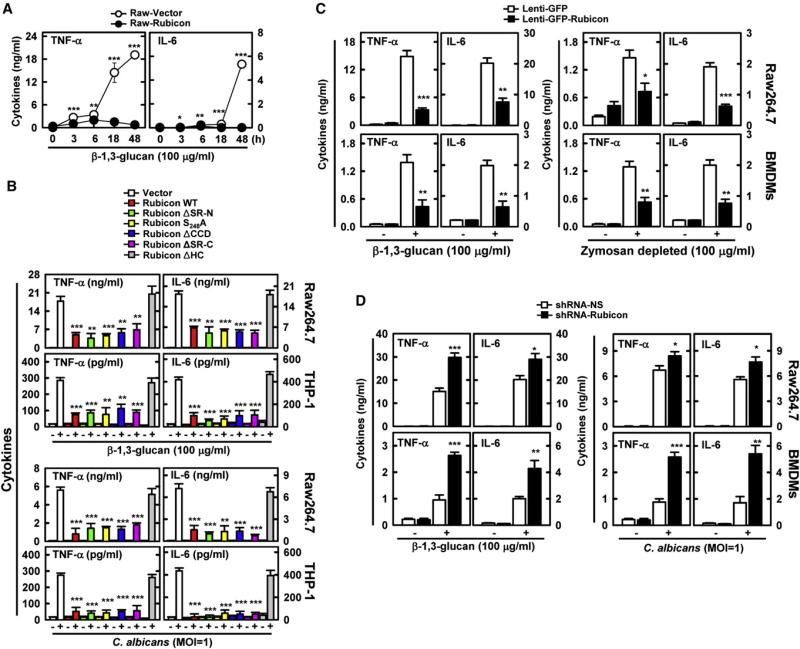
Figure 4. Negative Effect of Rubicon on Host Antifungal Immunity in a CARD9 Binding-Dependent Manner.
(A) Decrease of Dectin-1 pathway-induced cytokine productions by Rubicon. Raw264.7 cells containing vector or Rubicon were stimulated with β-1,3-glucan for ELISA. Additional data are shown in Figures S4A and S4B.
(B) Decrease of Dectin-1 pathway-induced cytokine productions by Rubicon. Raw264.7 cells and THP-1 cells containing vector, Rubicon WT, or its mutants were stimulated with β-1,3-glucan or C. albicans infection for cytokine production by ELISA. Additional data are shown in Figure S4C.
(C) Rubicon expression decreases cytokine productions induced by β-1,3-glucan or zymosan depleted by hot alkali treatment. Raw264.7 cells and BMDMs infected with lenti-GFP or lenti-GFP-Rubicon were stimulated with β-1,3-glucan or zymosan depleted by hot alkali treatment for cytokine ELISA.
(D) Depletion of Rubicon expression increases Dectin-1 pathway-induced cytokine productions. Raw264.7 cells and BMDMs lentivirus-shRNA-NS or lentivirus-shRNA-Rubicon were stimulated with β-1,3-glucan or C. albicans infection for cytokine ELISA. The data are the mean ± SD of values from three experiments.
*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 compared with the control. See also Figure S4.