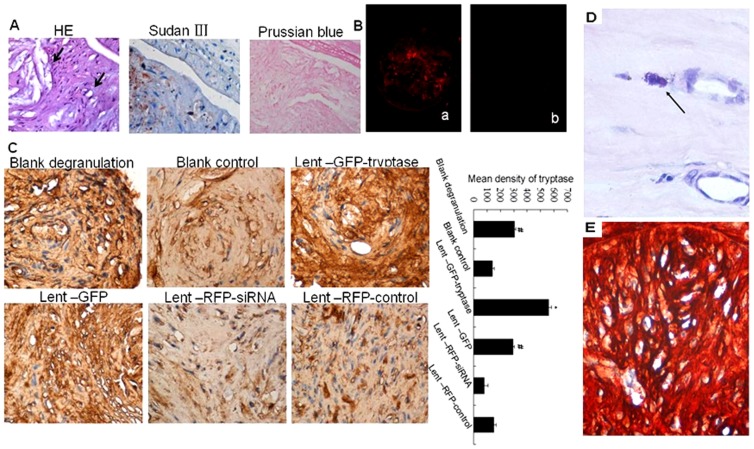
Figure 2. Effects of lentivirus carriers in apoE-/- mice by tail vein injection.
A. Formation of atherosclerotic plaques in cervical arteries. Black arrows in the HE section (×400) show the cholesterol crystals (the upper arrow) and foam cells(the lower arrow). Lipids in the plaque show orange-red by Sudan III stain(×400). Prussian blue stain shows negative results in the plaque (×400). B. ApoE-/- mouse cervical artery frozen section observed under a fluorescent microscope. Red fluorescence can be observed in the plaque after letivirus injection. a. RFP expression in the plaque of the Lent-RFP-controlsiRNA mouse detected under a fluorescent microscope (×100). b. No RFP expression was observed in the plaque of the blank control mouse (×100). C. Immunohistochemical stain of tryptase stain in the atherosclerotic plaques. Tryptase expression showed the highest level in the Lent-GFP-tryptase group, while the lowest level was found in the Lent-RFP-siRNA group. *P<0.01 vs. other groups (n = 5). #P<0.05 vs. blank control, Lent-RFP-siRNA and Lent-RFP-control (n = 5).D. Mast cell aggregation in the atherosclerotic plaques. Toluidine Blue staining showed activated and degranulating mast cells (arrow, ×800). E. Double stain of tryptase and GFP in the plaques (×400). The stain of tryptase and GFP using AEC or DAB as enzyme substrates showed red or brown respectively. The colour of red brown showed in the plaque because of the two colours overlapped, which indicated the co-localization of the two proteins.