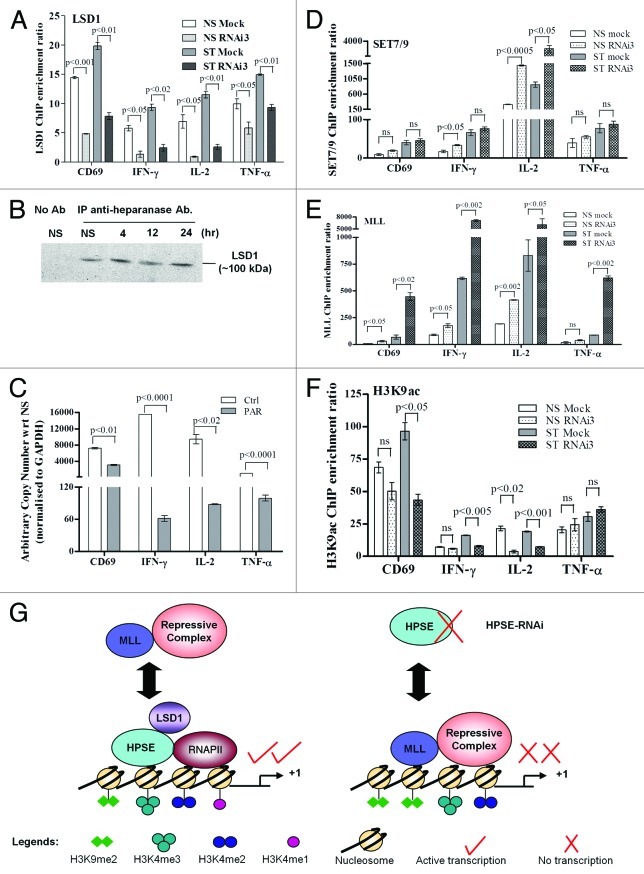
Figure 6. Nuclear heparanase may control H3 methylation profiles by recruiting LSD1 and excluding MLL from gene promoters in T cells. (A) LSD1 ChIP assays were performed on Jurkat T cells transfected with heparanase RNAi3 or a negative siRNA control (Mock). Real-time PCR was performed using primers covering the -0.15 kb proximal promoter of the CD69, IFN-γ, IL-2 and TNF-α genes. (B) Immunoprecipitation of heparanase from cross-linked sonicated nuclear lysates of either NS or PI-treated T cells followed by immunoblot analysis with an anti-LSD1 antibody. No antibody (no Ab) was used as a negative control. (C) Jurkat T cells untreated (Ctrl) or pre-treated with 3 mM pargyline (PAR) and non-stimulated or stimulated with PI for 2 h. Total RNA was extracted and TaqMan real-time PCR performed for CD69, IFN-γ, IL-2 and TNF-α transcripts. Results are plotted as arbitrary copies relative to the corresponding NS sample and normalized to GAPDH. (D) SET7/9, (E) MLL and (F) H3K9ac ChIP assays were performed as in (A). Data represent the mean ± SE of three independent experiments. (G) Proposed model of the interplay of nuclear heparanase with LSD1, RNAP II, MLL and histone methylation marks.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.