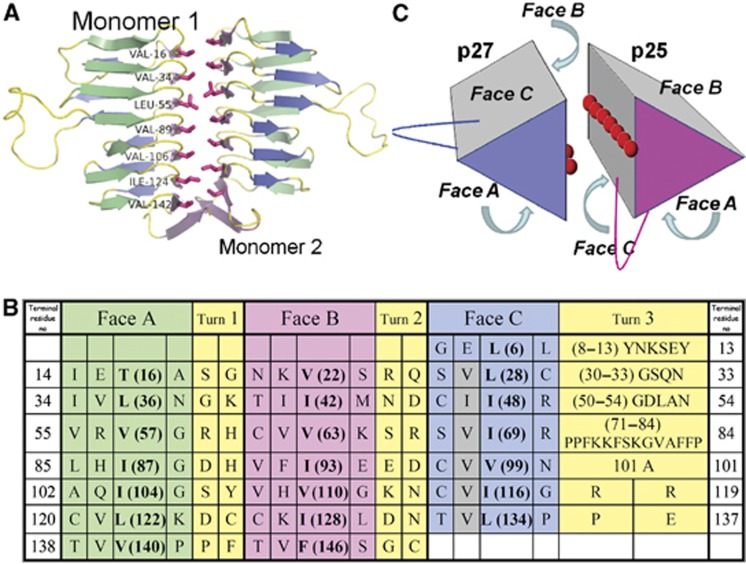
Figure 5.
A proposed dimerization mode for p27 and p25. (A) The crystallographic p27 homodimer, visualized perpendicular to the dimerization axis with the residues of the hydrophobic ridge on the B face highlighted. (B) Structure-based amino-acid sequence alignment of the seven ‘rungs’ of p25. β-helix faces are coloured as in Figure 4. The grey shading indicates the hydrophobic amino acids in Face C that are predicted to form the dimer interface. Amino acids that face the interior of the β-helix and thus contribute to the hydrophobic core are indicated in bold. (C) A model of the physiological p27/p25 heterodimer. The hydrophobic amino acids exposed on the surfaces of Faces B and C of p27 and p25 (respectively) are depicted with red spheres. The locations of the two edges that contain extended loops (between faces A and C) are also indicated.