Figure 1.
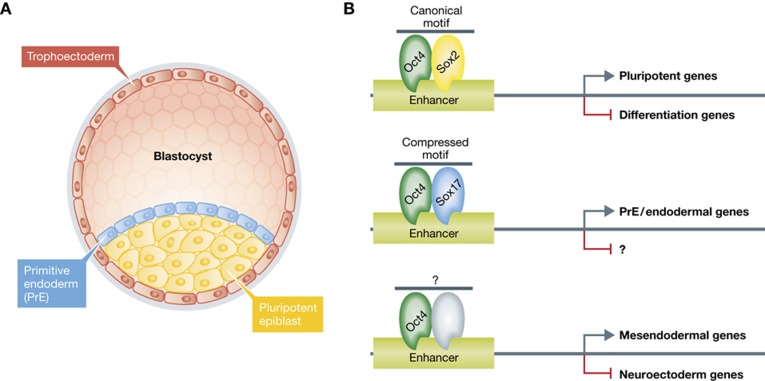
Oct4 regulates pluripotency and early development. (A) During early development the mouse late blastocyst comprises three distinct lineages: (1) the epiblast, which gives rise to the embryo proper, (2) primitive endoderm and (3) trophectoderm giving rise to extraembryonic cell types of placenta and yolk sac. (B) Model for cooperative action of Oct4 and Sox transcription factors in pluripotency and during lineage fate choice based on this study. In epiblast and ESCs, the cooperative binding of Oct4/Sox2 complex to canonical motif-containing enhancers facilitates pluripotency maintenance by up- and downregulation of pro-pluripotent and differentiation factors, respectively. Upon induction of PrE, Sox17 levels increase and directly recruit oct4 to compressed motif-containing enhancers, which positively regulate a set of PrE-specification genes (this study), and likely negatively regulate other yet to be defined genes. Notably, Oct4 can also drive commitment into the mesendodermal cell fate and repress neuroectodermal lineage by an undefined partner (Thomson et al, 2011).