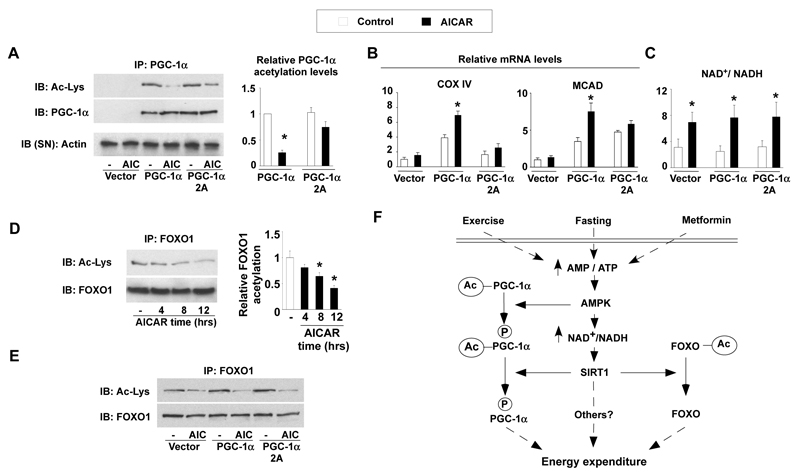
Figure 4. The PGC-1α phosphorylation mutant is resistant to deacetylation.
(A) C2C12 myocytes were transfected with the wild-type or the 2A mutant form of PGC-1α, using empty vector as control. After 36hrs, cells were treated with AICAR and total lysates were used to test PGC-1α acetylation. Relative acetylation levels of PGC-1α are shown on the right. (B) Cells were treated as in (A), and, after AICAR treatment, target mRNA levels were analyzed by RT-Q-PCR. (C) Cells were treated as in (A), and acidic or alkali lysates were obtained to measure NAD+ and NADH. (D) C2C12 myotubes were treated with AICAR for the times indicated. Then, total protein lysates were used for immunoprecipitation of FOXO1. Relative FOXO1 acetylation is shown on the right (E) As in (A), but immunoprecipitations were performed against FOXO1. (F) Scheme illustrating the convergent actions of AMPK and SIRT1 on PGC-1α. Pharmacological (metformin) and physiological (fasting or exercise) activation of AMPK in muscle triggers an increase in the NAD+/NADH ratio, which activate SIRT1. AMPK also induces the phosphorylation of PGC-1α and primes it for subsequent deacetylation by SIRT1. The impact of AMPK and SIRT1 on the acetylation status of PGC-1α and other transcriptional regulators, such as the FOXO family of transcription factors, will then modulate mitochondrial function and lipid metabolism. All values are presented as mean+/-SE. * indicates statistical difference vs. corresponding vehicle group at P<0.05.