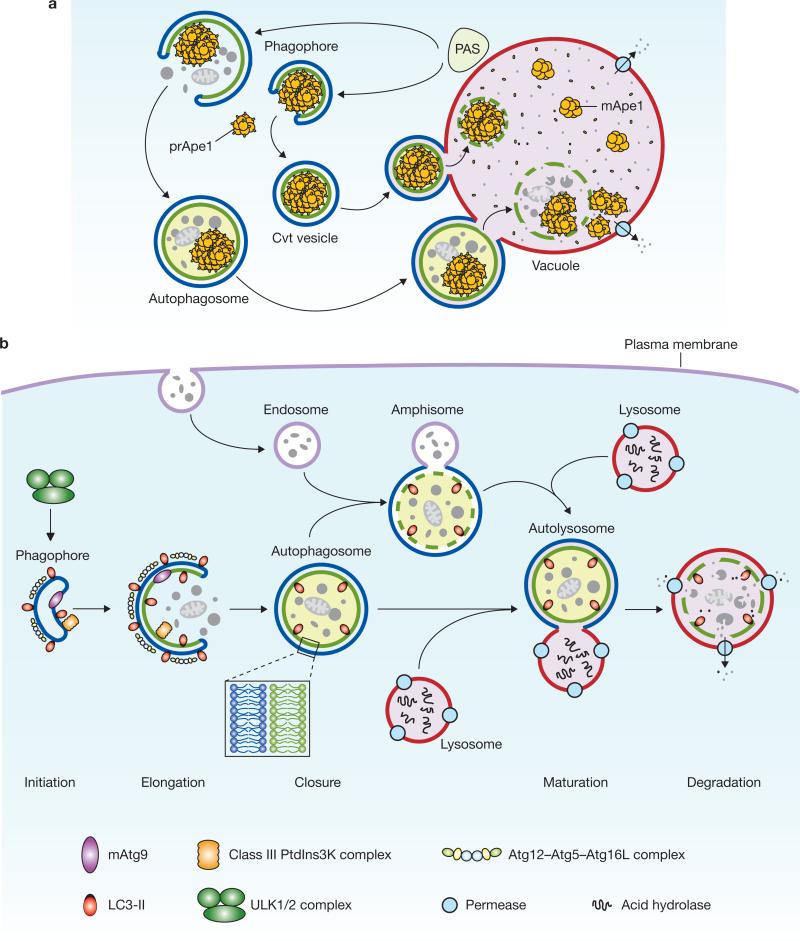
Figure 1.
Schematic depiction of autophagy. (a) In yeast, both autophagy and the Cvt pathway engulf cargoes within distinct double-membrane vesicles, which are thought to originate from the phagophore assembly site (PAS). The PAS is defined as the initial site for autophagy-related (Atg) protein recruitment. The Cvt pathway is one example of selective autophagy, and the only example of a biosynthetic autophagy-related pathway. The Cvt vesicle (140–160 nm in diameter) appears to closely enwrap the specific cargo — the Cvt complex (consisting of the precursor form of aminopeptidase I — prApe1 — and the Atg19 receptor), and exclude bulk cytoplasm. The autophagosome (300–900 nm in diameter) engulfs cytoplasm, including organelles, and also the Cvt complex. The completed vesicles then fuse with the vacuole, the yeast analogue of the mammalian lysosome, and release the inner single-membrane vesicle (autophagic or Cvt body) into the lumen. Subsequent breakdown of the inner vesicles allows the maturation of prApe1 and the degradation of cytoplasm, and hence the recycling of the resulting macromolecules through vacuolar permeases. (b) Mammalian autophagy is initiated by the formation of the phagophore, followed by a series of steps, including the elongation and expansion of the phagophore, closure and completion of a double-membrane autophagosome (which surrounds a portion of the cytoplasm), autophagosome maturation through docking and fusion with an endosome (the product of fusion is known as an amphisome) and/or lysosome (the product of fusion is known as an autolysosome), breakdown and degradation of the autophagosome inner membrane and cargo through acid hydrolases inside the autolysosome, and recycling of the resulting macromolecules through permeases. So far, there is no evidence for a PAS that exists in mammalian cells, and so the mammalian phagophore could be equivalent to the yeast PAS, or derived from the PAS. The core molecular machinery is also depicted, such as the ULK1 and ULK2 complexes that are required for autophagy induction, class III PtdIns3K complexes that are involved in autophagosome formation, mammalian Atg9 (mAtg9) that potentially contributes to the delivery of membrane to the forming autophagosome and two conjugation systems, the LC3-II and Atg12–Atg5–Atg16L complex, which are proposed to function during elongation and expansion of the phagophore membrane.