Abstract
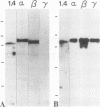
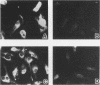
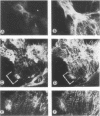
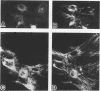
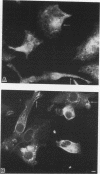
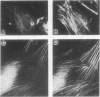
Protein kinase C (PKC)1 isozymes comprise a family of related cytosolic kinases that translocate to the cell particulate fraction on stimulation. The activated enzyme is thought to be on the plasma membrane. However, phosphorylation of protein substrates occurs throughout the cell and is inconsistent with plasma membrane localization. Using an isozyme-specific monoclonal antibody we found that, on activation, this PKC isozyme translocates to myofibrils in cardiac myocytes and to microfilaments in fibroblasts. Translocation of this activated PKC isozyme to cytoskeletal elements may explain some of the effects of PKC on cell contractility and morphology. In addition, differences in the translocation site of individual isozymes--and, therefore, phosphorylation of different substrates localized at these sites--may explain the diverse biological effects of PKC.
Full text
PDF


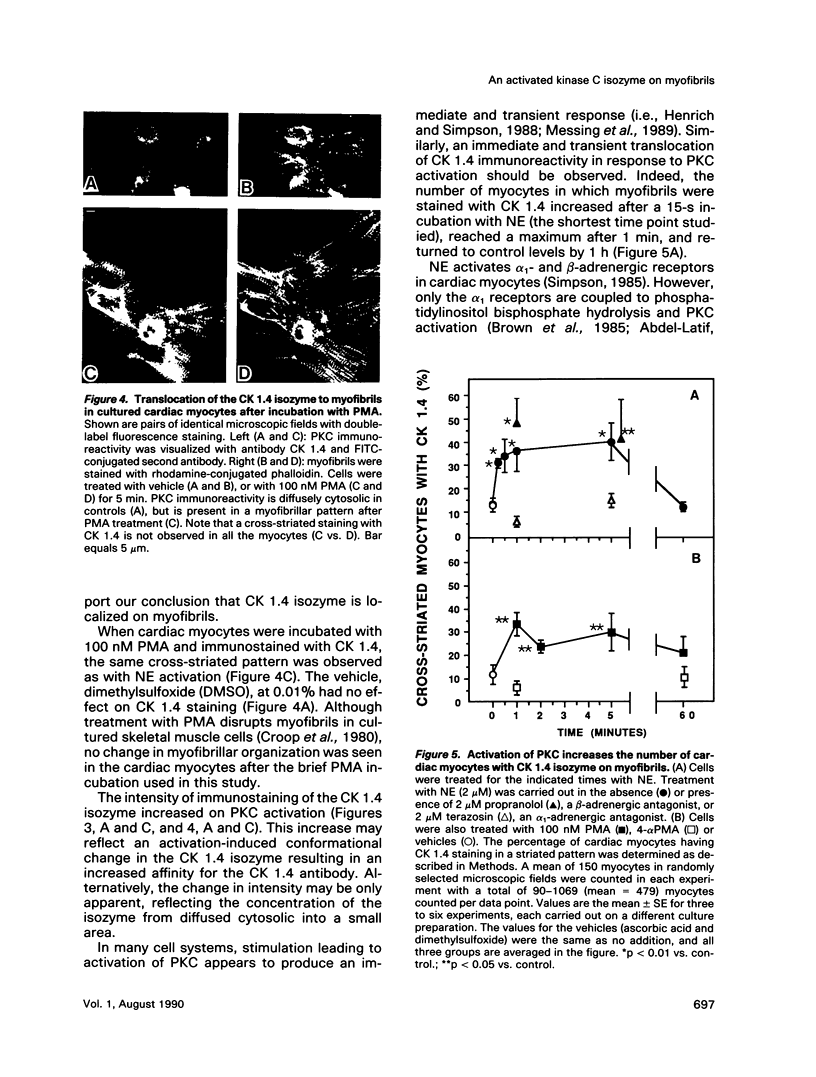
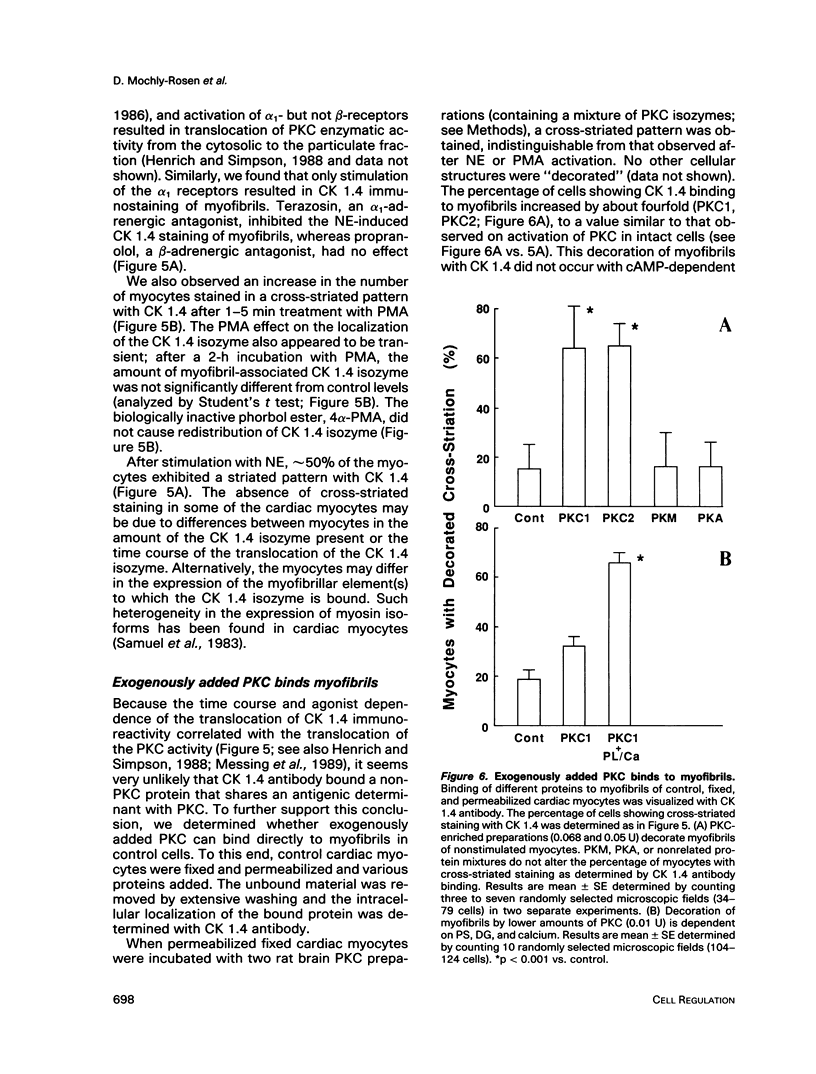
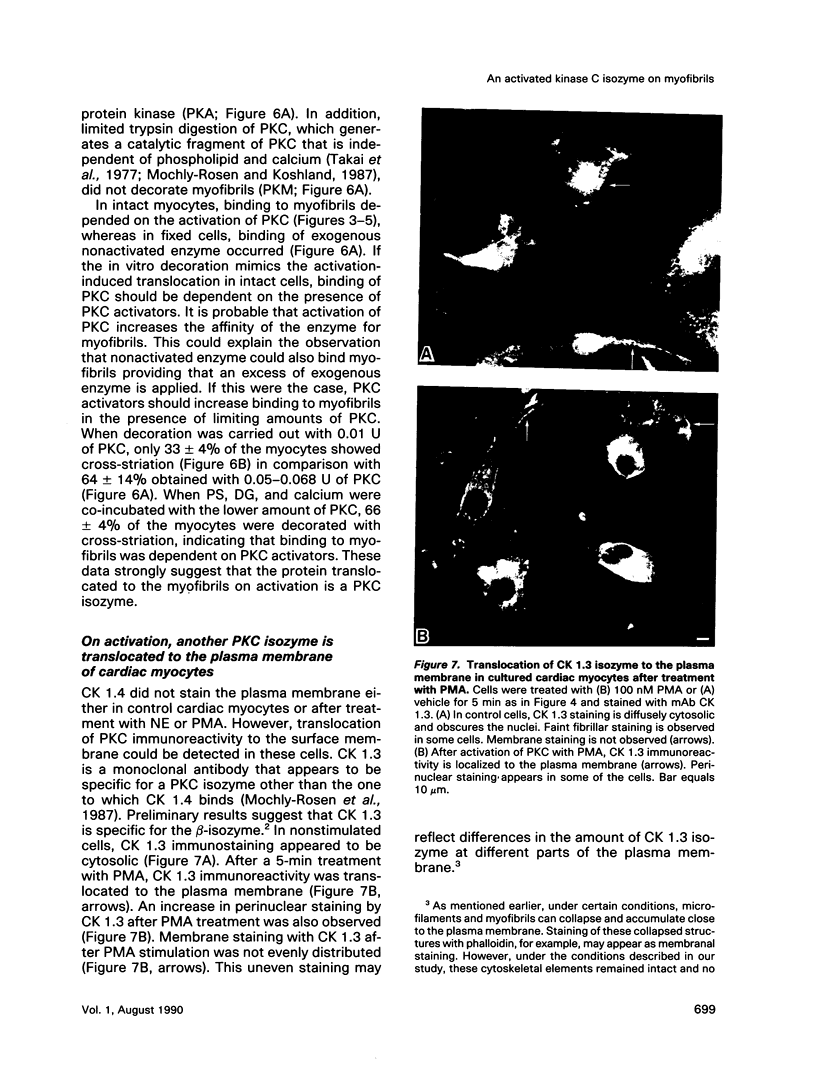
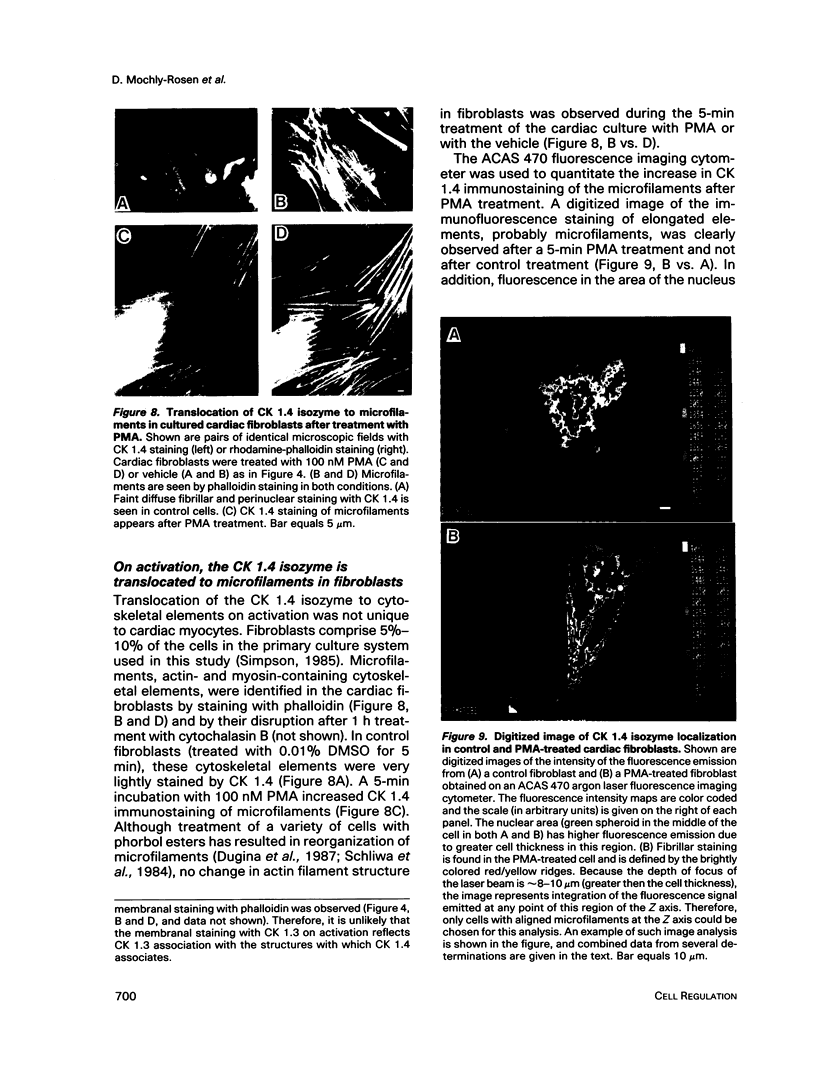






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Latif A. A. Calcium-mobilizing receptors, polyphosphoinositides, and the generation of second messengers. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Sep;38(3):227–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad Z., Lee F. T., DePaoli-Roach A., Roach P. J. Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase by the Ca2+- and phospholipid-activated protein kinase (protein kinase C). J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8743–8747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen I. S., Cohen N. M., Dhallan R. S., Gaa S. T., Lederer W. J., Rogers T. B. Angiotensin II increases spontaneous contractile frequency and stimulates calcium current in cultured neonatal rat heart myocytes: insights into the underlying biochemical mechanisms. Circ Res. 1988 Mar;62(3):524–534. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.3.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader D., Masaki T., Fischman D. A. Immunochemical analysis of myosin heavy chain during avian myogenesis in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):763–770. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M. Protein kinase C activation by diacylglycerol second messengers. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):631–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90774-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Duerr A., Solomon F., Penman S. The outer boundary of the cytoskeleton: a lamina derived from plasma membrane proteins. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):859–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Alpha 1-adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis in adult rat cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 1985 Oct;57(4):532–537. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.4.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn P., Kupfer A., Singer S. J. Dynamic membrane-cytoskeletal interactions: specific association of integrin and talin arises in vivo after phorbol ester treatment of peripheral blood lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):497–501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn P. Phosphatidylinositol cycle and its possible involvement in the regulation of cytoskeleton-membrane interactions. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Jan;36(1):15–24. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240360103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn P., Rotman A., Meyer R. K., Burger M. M. Diacylglycerol in large alpha-actinin/actin complexes and in the cytoskeleton of activated platelets. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):469–472. doi: 10.1038/314469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Newell M. K., Justement L. B., McGuire J. C., Leach K. L., Chen Z. Z. Ia binding ligands and cAMP stimulate nuclear translocation of PKC in B lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):629–632. doi: 10.1038/327629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Z., McGuire J. C., Leach K. L., Cambier J. C. Transmembrane signaling through B cell MHC class II molecules: anti-Ia antibodies induce protein kinase C translocation to the nuclear fraction. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2345–2352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claycomb W. C., Moses R. L. Growth factors and TPA stimulate DNA synthesis and alter the morphology of cultured terminally differentiated adult rat cardiac muscle cells. Dev Biol. 1988 Jun;127(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croop J., Toyama Y., Dlugosz A. A., Holtzer H. Selective effects of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate on myofibrils and 10-nm filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5273–5277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugina V. B., Svitkina T. M., Vasiliev J. M., Gelfand I. M. Special type of morphological reorganization induced by phorbol ester: reversible partition of cell into motile and stable domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4122–4125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsey D. L., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F., Blackshear P. J. Protein kinase C in fibroblasts. Characteristics of its intracellular location during growth and after exposure to phorbol esters and other mitogens. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2234–2243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich C. J., Simpson P. C. Differential acute and chronic response of protein kinase C in cultured neonatal rat heart myocytes to alpha 1-adrenergic and phorbol ester stimulation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1988 Dec;20(12):1081–1085. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(88)90588-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L., Ives H. E. Growth inhibition by protein kinase C late in mitogenesis. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):849–850. doi: 10.1038/329849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. L., Yoshida Y., Nakabayashi H., Knopf J. L., Young W. S., 3rd, Huang K. P. Immunochemical identification of protein kinase C isozymes as products of discrete genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 31;149(3):946–952. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90500-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Ling N., Cooper J. A. Protein kinase C phosphorylation of the EGF receptor at a threonine residue close to the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):480–483. doi: 10.1038/311480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Tanaka T., Yoshida T., Onoda K., Ohta H., Hagiwara M., Itoh Y., Ogura M., Saito H., Hidaka H. Immunocytochemical evidence for translocation of protein kinase C in human megakaryoblastic leukemic cells: synergistic effects of Ca2+ and activators of protein kinase C on the plasma membrane association. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):929–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaken S., Leach K., Klauck T. Association of type 3 protein kinase C with focal contacts in rat embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):697–704. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Stossel T. P. Modulation of gelsolin function by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):362–364. doi: 10.1038/325362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Wise B. C., Kuo J. F. Phosphorylation of cardiac troponin inhibitory subunit (troponin I) and tropomyosin-binding subunit (troponin T) by cardiac phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):189–195. doi: 10.1042/bj2090189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. U., Zimmermann A., Cottier H. Phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) suppresses polarization and locomotion and alters F-actin content of Walker carcinosarcoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1985 Oct 15;36(4):495–501. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley S. C., Jaken S. Activation of alpha-protein kinase C leads to association with detergent-insoluble components of GH4C1 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jan;4(1):59–68. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka Y., Ogita K., Ase K., Nomura H., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. The heterogeneity of protein kinase C in various rat tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 30;151(3):973–981. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80461-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassing I., Lindberg U. Specific interaction between phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and profilactin. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):472–474. doi: 10.1038/314472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach K. L., Powers E. A., Ruff V. A., Jaken S., Kaufmann S. Type 3 protein kinase C localization to the nuclear envelope of phorbol ester-treated NIH 3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):685–695. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leatherman G. F., Kim D., Smith T. W. Effect of phorbol esters on contractile state and calcium flux in cultured chick heart cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 2):H205–H209. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.1.H205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim M. S., Sutherland C., Walsh M. P. Phosphorylation of bovine cardiac C-protein by protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):1187–1195. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91932-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limas C. J., Limas C. Carbachol induces desensitization of cardiac beta-adrenergic receptors through muscarinic M1 receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):699–704. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. D., Wood J. G., Raynor R. L., Wang Y. C., Noland T. A., Jr, Ansari A. A., Kuo J. F. Subcellular distribution and immunocytochemical localization of protein kinase C in myocardium, and phosphorylation of troponin in isolated myocytes stimulated by isoproterenol or phorbol ester. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1105–1110. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90787-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzei G. J., Kuo J. F. Phosphorylation of skeletal-muscle troponin I and troponin T by phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase and its inhibition by troponin C and tropomyosin. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):361–369. doi: 10.1042/bj2180361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing R. O., Stevens A. M., Kiyasu E., Sneade A. B. Nicotinic and muscarinic agonists stimulate rapid protein kinase C translocation in PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1989 Feb;9(2):507–512. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-02-00507.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Basbaum A. I., Koshland D. E., Jr Distinct cellular and regional localization of immunoreactive protein kinase C in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4660–4664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Koshland D. E., Jr A general procedure for screening inhibitory antibodies: application for identifying anti-protein kinase C antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1988 Apr;170(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90085-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Koshland D. E., Jr Domain structure and phosphorylation of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2291–2297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa M., Hidaka H., Adelstein R. S. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle heavy meromyosin by calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. The effect on actin-activated MgATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14069–14072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta Y., Akiyama T., Nishida E., Sakai H. Protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase induce opposite effects on actin polymerizability. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80391-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The structure, expression, and properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Hall P. F. Isolation and characterization of protein kinase C from Y-1 adrenal cell cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):553–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patskan G. J., Baxter C. S. Specific stimulation of histone H2B and H4 phosphorylation in mouse lymphocytes by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):12899–12903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppers S. C., Holz R. W. Catecholamine secretion from digitonin-treated PC12 cells. Effects of Ca2+, ATP, and protein kinase C activators. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14665–14669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel J. L., Rappaport L., Mercadier J. J., Lompre A. M., Sartore S., Triban C., Schiaffino S., Schwartz K. Distribution of myosin isozymes within single cardiac cells. An immunohistochemical study. Circ Res. 1983 Feb;52(2):200–209. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M., Nakamura T., Porter K. R., Euteneuer U. A tumor promoter induces rapid and coordinated reorganization of actin and vinculin in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1045–1059. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz J., Schaefer B., Schmitz W., Scholz H., Steinfath M., Lohse M., Schwabe U., Puurunen J. Alpha-1 adrenoceptor-mediated positive inotropic effect and inositol trisphosphate increase in mammalian heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Apr;245(1):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearman M. S., Naor Z., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Differential expression of multiple protein kinase C subspecies in rat central nervous tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):911–919. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P., Savion S. Differentiation of rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating nonmyocardial cells. Cross-striations, ultrastructure, and chronotropic response to isoproterenol. Circ Res. 1982 Jan;50(1):101–116. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. Stimulation of hypertrophy of cultured neonatal rat heart cells through an alpha 1-adrenergic receptor and induction of beating through an alpha 1- and beta 1-adrenergic receptor interaction. Evidence for independent regulation of growth and beating. Circ Res. 1985 Jun;56(6):884–894. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starksen N. F., Simpson P. C., Bishopric N., Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Cardiac myocyte hypertrophy is associated with c-myc protooncogene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8348–8350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden D., Vanecek J., Klein D. C., Thomas T. P., Anderson W. B. Activation of protein kinase C potentiates isoprenaline-induced cyclic AMP accumulation in rat pinealocytes. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):359–361. doi: 10.1038/314359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Inoue M., Nishizuka Y. Studies on a cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase and its proenzyme in mammalian tissues. I. Purification and characterization of an active enzyme from bovine cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7603–7609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. Interaction of protein kinase C with membranes is regulated by Ca2+, phorbol esters, and ATP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15718–15722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., Sahyoun N. Protein kinase C and phosphatidylserine bind to Mr 110,000/115,000 polypeptides enriched in cytoskeletal and postsynaptic density preparations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13327–13332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Iida K., Janmey P. A. Identification of a polyphosphoinositide-modulated domain in gelsolin which binds to the sides of actin filaments. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):805–812. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan S. H., Sunahara F. A., Sen A. K. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters inhibit cardiac functions and induce redistribution of protein kinase C in perfused beating rat heart. Circ Res. 1987 Sep;61(3):372–378. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan S., Sen A. K. Characterization of the membrane-bound protein kinase C and its substrate proteins in canine cardiac sarcolemma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 8;886(1):152–161. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalewski P. D., Forbes I. J., Valente L., Apostolou S., Hurst N. P. Translocation of protein kinase C to a Triton-insoluble sub-cellular compartment induced by the lipophilic gold compound auranofin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 1;37(7):1415–1417. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]