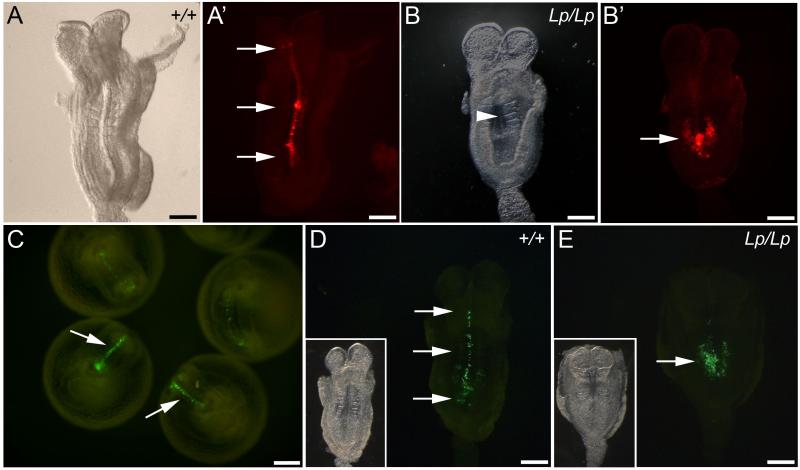
Fig. 4. Assessment of PCP phenotype in DiI-labelled and GFP-electroporated embryos after culture.
(A,A’) Bright field and fluorescence images of flat mounted wild type embryo. DiI-labelled cells extend rostral to the node (arrows in A’), indicating normal CE and axial elongation. (B,B’) Bright field and fluorescence images of a loop-tail homozygous mutant. The embryo displays failure of Closure 1 (arrowhead in B indicates open neural tube) and very limited midline extension of DiI-labelled cells (arrow in B’). (C) Wild type embryos cultured for 18-20 h following electroporation of a GFP-expression vector into the caudal neural plate. GFP-labelled cells extend along the midline (arrows). (D,E) Fluorescence (inset: bright-field) images of embryos following GFP electroporation. The wild type embryo (D) displays marked extension of GFP-labelled cells along the neural plate midline (arrows), whereas the loop-tail homozygous embryo (E) has undergone minimal axial extension of GFP-positive cells (arrow). Scale bars represent: 200 μm in A-E.