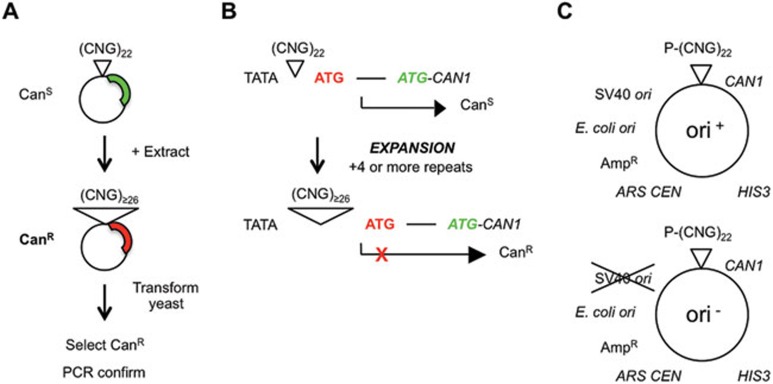
Figure 1.
Key features of the in vitro assay for expansions. (A) Assay procedure. A 22-repeat shuttle vector was incubated with cell-free extract, then recovered and transformed into yeast. Plasmids containing an expanded (≥ 26) repeat confer canavanine resistance. The repeat region is amplified by PCR and the expansion is confirmed on polyacrylamide gels. (B) Expansion selection22. At 22 repeats, CAN1 is expressed, causing canavanine sensitivity. Expansions adding ≥ 4 repeats cause a change in the transcriptional start site, such that an out-of-frame initiator codon is incorporated into the mRNA. Translation from this initiator codon is out-of-frame with respect to the CAN1 structural gene, causing canavanine resistance22. (C) Shuttle vectors. Plasmids are based on those used by Claassen and Lahue35, modified with CAN1 selection cassette22. Briefly, each plasmid is a three-way shuttle vector capable of replicating in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, E. coli, and human cells or cell-free extracts supplemented with SV40 large T antigen. The TNR is usually (CTG)22, although other sequences can be substituted. P, adh1 promoter for expression in yeast.