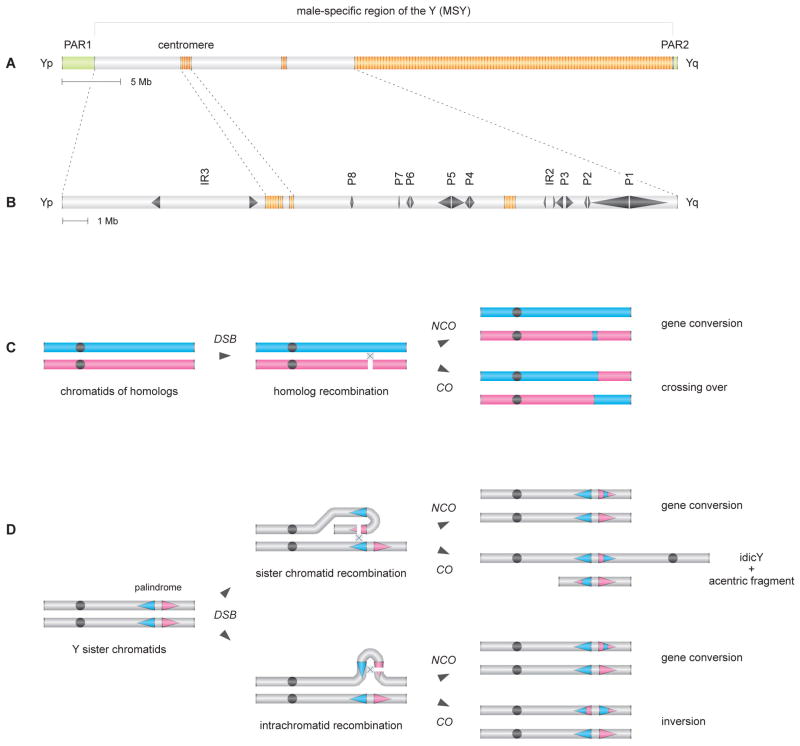
Figure 1. Hypothesized mechanism of idicY formation by homologous recombination in MSY palindrome.
(A) Schematic representation of chrY. MSY is flanked by pseudoautosomal regions PAR1 and PAR2 (green) and contains heterochromatic blocks (orange). Yp, short arm. Yq, long arm.
(B) Expanded view of MSY euchromatin, with palindromes P1 through P8 and inverted repeats IR2 and IR3.
(C) Conventional recombination between homologous chromosomes: DSB resolution by NCO and CO pathways yielding, respectively, gene conversion and crossing over. Second chromatid not shown for each of the two homologs.
(D) Model of homologous recombination in MSY palindromes: DSB resolution by NCO pathways yields gene conversion. Resolution by crossing over between sister chromatids can produce an idicY (and an acentric fragment), while crossing over within a chromatid yields an inversion.