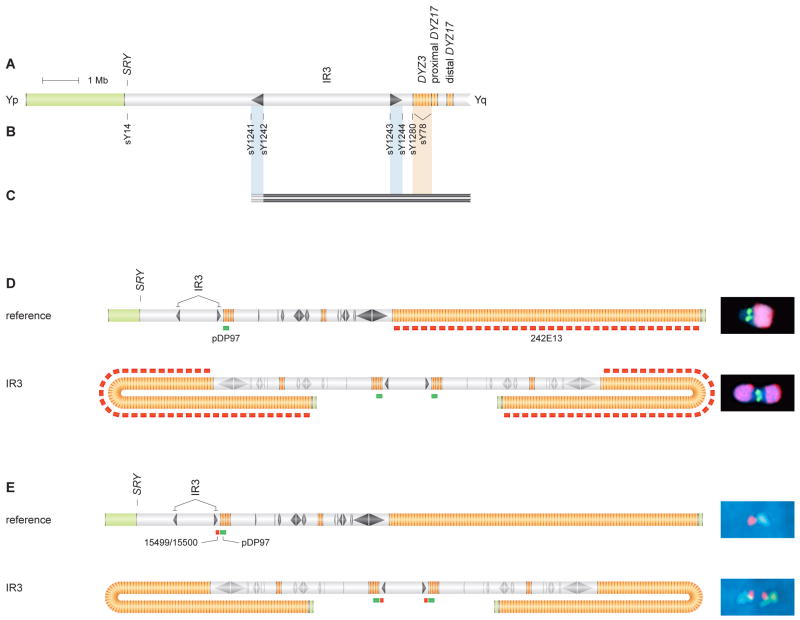
Figure 5. IdicYq chromosomes formed by crossing over between sister chromatids at Yp inverted repeat: STS content and FISH analyses.
(A) Schematic representation of Yp and centromeric region.
(B) STSs employed in mapping deletion breakpoints in two individuals in whom sY14 (SRY) was absent, and sY78 and sY1273 (Figure 2) were present. These STSs include boundary and spacer-flanking markers for IR3 inverted repeat and a marker in Yp pericentromeric euchromatin.
(C) Results of testing DNAs from two patients for presence or absence of STSs. Solid black bars encompass STSs found to be present. Gray bars indicate breakpoint intervals within IR3's distal arm that could not be further narrowed due to cross-amplification of identical sequences in IR3's proximal arm. See Figure S6 for identifiers of patients tested.
(D) Hybridization of probes pDP97 (to centromeric DYZ3 repeats), in green, and 242E13 (to DYZ1 repeats in distal Yq heterochromatin), in red, to metaphase chrY of normal male (above) and to idicYq with breakpoint in IR3 (below). (Metaphase FISH precludes resolution of two centromeric signals in this idicYq.) All images at same magnification.
(E) Interphase FISH demonstrates duplication of sequences proximal to IR3 in idicYq. Hybridization of probes 15499/15500 (proximal to IR3), in red, and pDP97, in green, produced expected patterns of red-green on chrY of normal male (above) and green-red-red-green on idicYq with breakpoint in IR3 (below). All images at same magnification. Two hundred nuclei were scored (Figure S7).