Fig. 3.
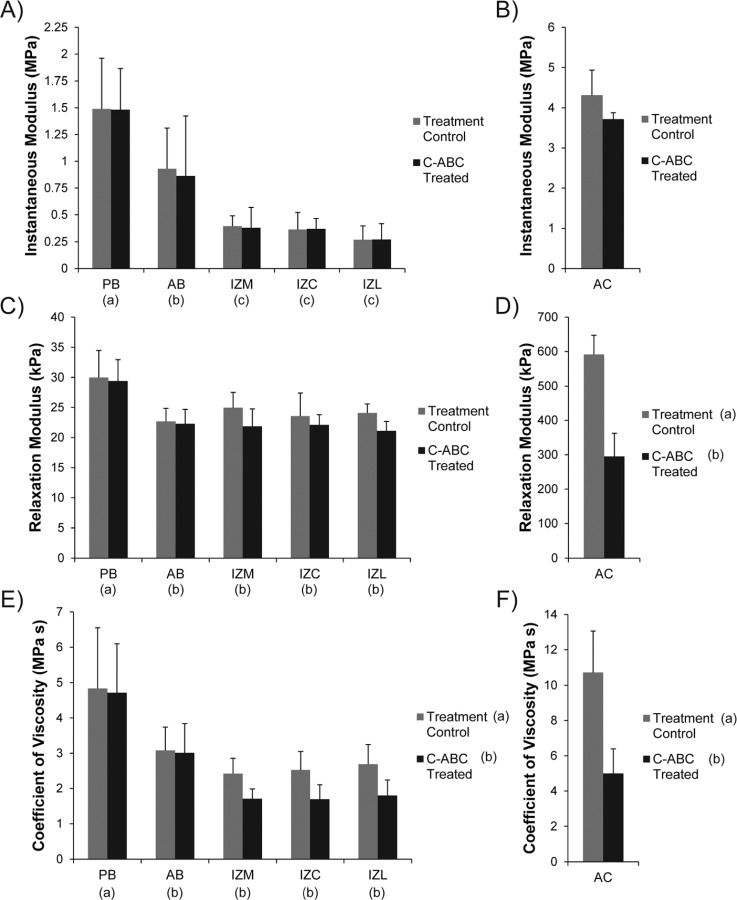
Viscoelastic compressive properties of GAG depleted TMJ disc and hyaline cartilage samples. (a) GAG removal with C-ABC did not produce a significant difference in the instantaneous modulus of the TMJ disc. (b) C-ABC treatment also had no effect on the instantaneous modulus of the tibial cartilage, although it did trend lower. (c) Overall, C-ABC treatment did not produce a change in the relaxation modulus of TMJ disc samples. (d) GAG depletion in articular cartilage produced a ∼50% decrease in the tissue's relaxation modulus. (e) GAG depletion produced an overall decrease in the coefficient of viscosity for TMJ disc samples. All regions of the intermediate zone (IZM, IZC, IZL) displayed a 30% decrease in viscosity. (f) C-ABC treatment of hyaline cartilage led to a ∼50% decrease in the coefficient of viscosity. Data is presented as mean ± SD. Letters in brackets represent the results of a two-way ANOVA for TMJ disc specimens and a student's t-test for hyaline cartilage specimens. Groups not connected by the same letter are statistically different. (Note: TMJ disc regions and hyaline cartilage are plotted different scales to enhance readability).
