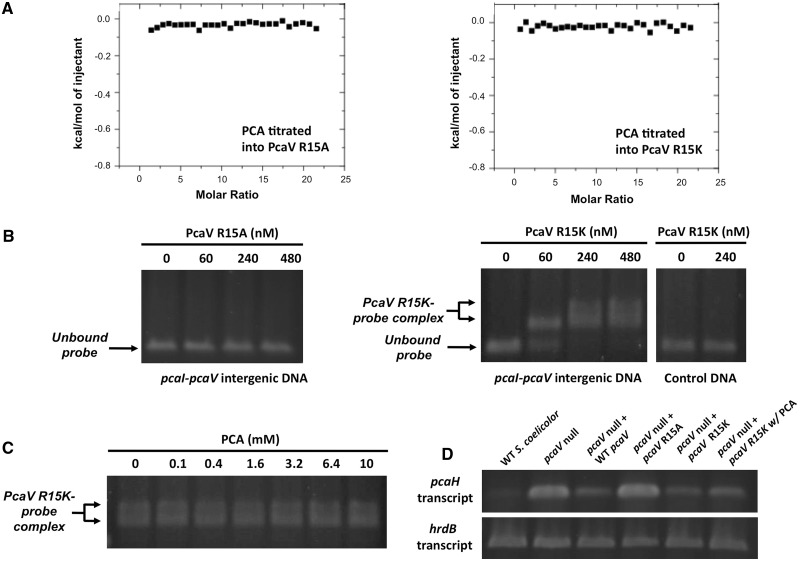
Figure 4.
PcaV Arg15 is a critical determinant for both ligand and DNA binding. (A) Representative binding isotherm of PCA titrated into PcaV R15A and PcaV R15K. Raw data are shown in Supplementary Figure S6C. (B) Agarose EMSA experiments using a PCR-amplified DNA probe spanning the pcaV–pcaI intergenic region and increasing concentrations of either PcaV R15A or R15K. In comparison with the unbound DNA probe in the electrophoresis, retarded migration of the DNA probe was observed on addition of PcaV R15K but not PcaV R15A. The formation of the PcaV R15K–probe complex is indicated by a double arrow, whereas the unbound DNA is indicated with a single arrow. The control DNA probe spans a region of the pcaH open reading frame that does not contain PcaV operator sites. (C) Agarose EMSA experiments using PcaV R15K bound to the pcaV–pcaI intergenic probe and increasing concentrations of protocatechuate. No dissociation of PcaV R15K from the DNA is observed on addition of increasing amounts of protocatechuate. (D) Reverse transcription PCR analyses of the pcaH gene in WT S. coelicolor, the pcaV null strain and pcaV null strains expressing genes encoding PcaV, PcaV R15A, or PcaV R15K under the control of the constitutive promoter (ermEp*) from pIJ10257. As previously reported, transcription of the pcaH gene is not repressed in the pcaV null strain. This transcriptional defect is suppressed in pcaV null strains over-expressing genes encoding either PcaV or PcaV R15K, but not in a strain producing PcaV R15A. Addition of protocatechuate to the pcaV null strain producing PcaV R15K did not induce transcription of the pcaH gene. The hrdB gene, which encodes a vegetative sigma factor, was used as a control and is constitutively transcribed in all samples.