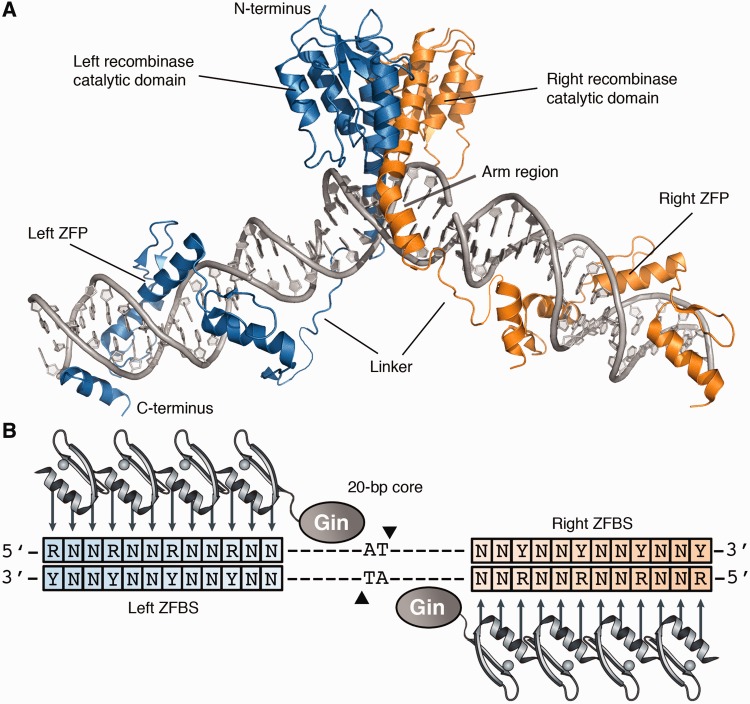
Figure 1.
Structure of the zinc-finger recombinase dimer bound to DNA. (A) Each ZFR monomer (blue or orange) consists of an activated serine recombinase catalytic domain linked to a custom-designed zinc-finger DNA-binding domain. Model was generated from crystal structures of the γδ resolvase and Aart zinc-finger protein (PDB IDs: 1GDT and 2I13, respectively). (B) Cartoon of the ZFR dimer bound to DNA. ZFR target sites consist of two-inverted ZFBS flanking a central 20-bp core sequence recognized by the ZFR catalytic domain. ZFPs can be designed to recognize distinct ‘left’ or ‘right’ half-sites (blue and orange boxes, respectively). Abbreviations are as follows: N indicates A, T, C or G; R indicates G or A; and Y indicates C or T.