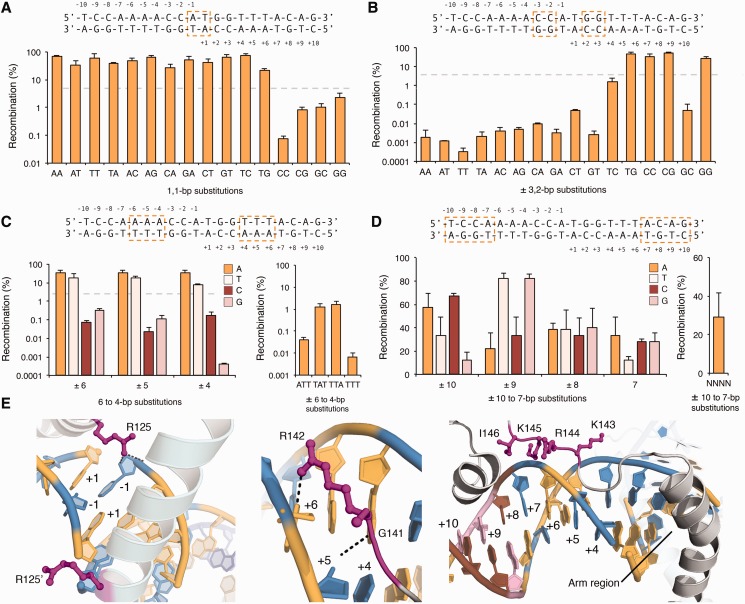
Figure 2.
Specificity of the Gin recombinase catalytic domain. (A–D) Recombination was measured on DNA targets that contained (A) each possible two-base combination at the dinucleotide core, (B) each possible two-base combination at positions 3 and 2, (C) each possible single-base substitution at positions 6, 5 and 4 and (D) each possible single-base substitution at positions 10, 9, 8 and 7. Substituted bases are boxed above each panel. Recombination was evaluated by split gene reassembly and measured as the ratio of carbenicillin-resistant to chloramphenicol-resistant transformants (‘Materials and Methods’ section). Dotted lines indicate threshold for which sequences were considered non-functional. Error bars indicate standard deviation (n = 3). (E) Interactions between the γδ resolvase dimer and DNA at (left) the dinucleotide core, (middle) positions 6, 5 and 4 and (right) positions 10, 9, 8 and 7 (PDB ID: 1GDT). Interacting residues are shown as magenta sticks. Bases are coloured as follows: A, yellow; T, blue; C, brown; and G, pink.