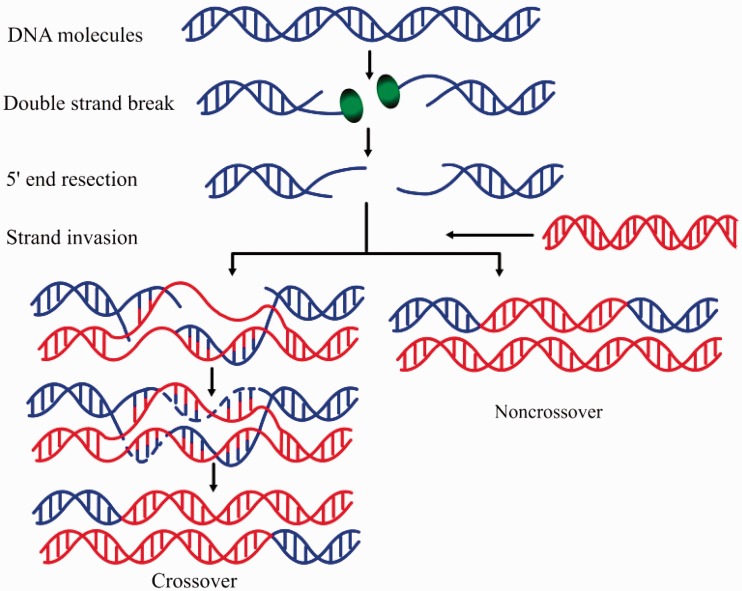
Figure 1.
A schematic drawing to show the meiotic recombination pathways in a DNA system. Recombination is initiated by a double-strand break (DSB) catalysed by the Spo11 protein (green ball), a relative of archaeal topoisomerase VI. After DSBs are formed, Spo11 is removed from the DNA molecule (blue helix) and the single-stranded 3′ ends are formed. These tails undergo strand invasion of intact homologous duplexes (red helix), ultimately yielding mature recombinant products. The repair of meiotic DSB can result in either reciprocal exchange of the chromosome arms flanking the break (a crossover) as shown in the left lower panel, or no exchange of flanking arms (a non-crossover or parental configuration) as shown in the right lower panel. Adapted from (2).