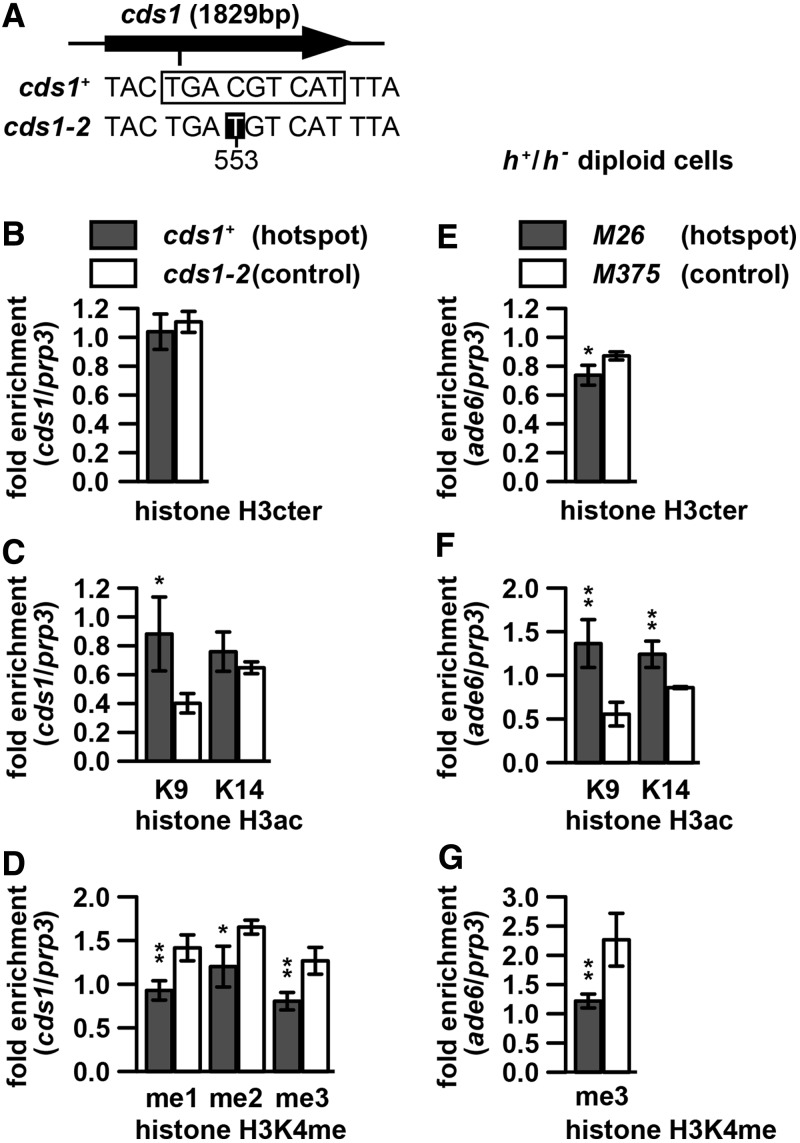
Figure 2.
Histone H3 and its modifications at the natural M26-sequence-dependent hotspot cds1-M26ES-I3 and at ade6-M26 in meiotic diploid cells. (A–D) Histone H3 and its modification levels around cds1-M26ES-I3 (cds1+, filled bars) and cds1-2 (open bars). cds1+ and cds1-2 cells in a pat1-114 background were cultured, and histone H3 and its modification levels were assessed by ChIP as in Figure 1H–J. (A) Positions of cds1-M26ES-I3 and cds1-2 within the cds1 gene and sequences around the two loci. The rectangle and white lettering indicate the M26-sequence and mutated base, respectively. ‘553’ indicates nucleotide position, with the first ‘A’ of the cds1 ORF as 1. Note that the M26-sequence at cds1-M26ES-I3 is present on both strands. (B) Levels of Histone H3 (C) Levels of H3K9ac and H3K14ac. (D) Levels of H3K4me1, H3K4me2 and H3K4me3. (E–G) Histone H3 and its modification levels in h+/h− meiotic cells around ade6-M26 (filled bars) and ade6-M375 (open bars). The ade6-M26 and ade6-M375 h+/h− diploid cells were induced to enter meiosis by nitrogen withdrawal and harvested 3 h after the induction. Histone H3 and its modification levels were assessed by ChIP as in Figure 1H–J. (E) Levels of Histone H3. (F) Levels of H3K9ac and H3K14ac. (G) Levels of H3K4me3.