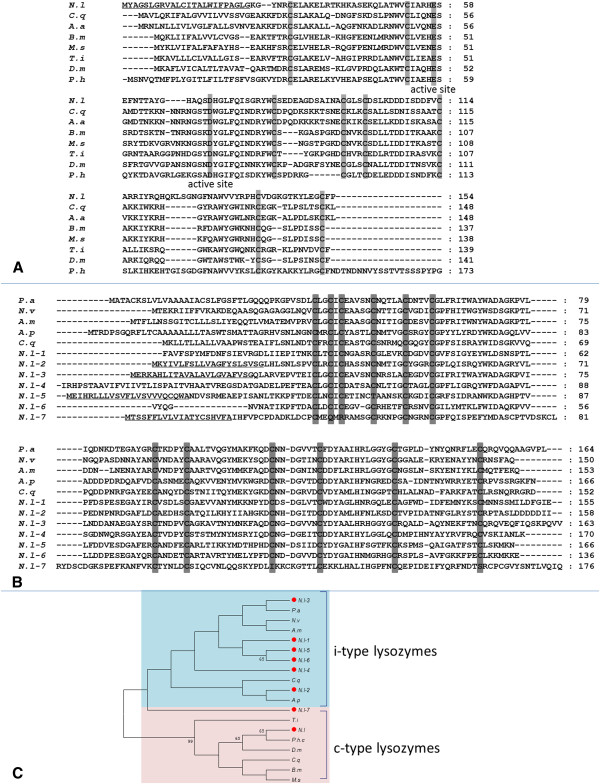
Figure 12.
Multiple sequence alignments of lysozymes of several insect species. (A) c-type lysozyme aligments; (B) i-type lysozyme aligments. The ClustalX program was used for alignments. The GenBank accession numbers for the sequences are as follows: Pediculus humanus corporis lysozyme P precursor (EEB19248); Bombyx mori lysozyme precursor (AAB40947); Manduca sexta lysozyme (AAB31190); Aedes aegypti lysozyme P (EAT44944), Triatoma infestans lysozyme (AAP83129), Culex quinquefasciatus lysozyme (EDS45638), Drosophila melanogaster lysozyme P (AAF47452), Periplaneta americana i-type lysozyme (AFI81521), C. quinquefasciatus lysozyme i-1 (EDS32730), Acyrthosiphon pisum lysozyme 1-like (XP_001949318), Nasonia vitripennis lysozyme 3-like (XP_001600829) and Apis mellifera lysozyme isoform 1 (XP_393161). The predicted signal peptide sequences of lysozymes are underlined. Gray shading indicates the conserved cysteine residues and the putative catalytic sites of the enzymes. (C) Phylogenetic analysis of insect c- and i-type lysozymes. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by Maximum likelihood, using the program Mega 5.05 (http://www.megasoftware.net/). The Jones-Taylor-Thornton (JTT) for amino acid substitution model was used, the test of phylogeny was done by the bootstrap method with 1000 replications, bootstrap values>50% are shown on each node of the tree. N.l, N. lugens; D.m, Drosophila melanogaster; A.p, Acyrthosiphon pisum; A.m, Apis mellifera; B.m, Bombyx mori; M. s, M. sexta; C. q, C. quinquefasciatus; T. i, T. infestans; A. a, A. aegypti; P. h. c, P. h. corporis; P. a, P. Americana and N. v, N. vitripennis.