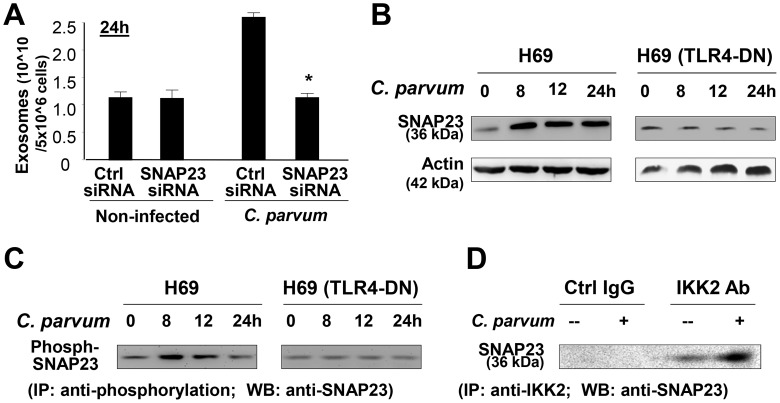
Figure 4. C. parvum-induced release of apical exosomes from biliary epithelial cells involves TLR4-dependent IKK2-SNAP23 interactions.
(A) SNAP23 siRNA inhibits C. parvum-induced release of apical exosomes. H69 monolayers were treated to a non-specific control siRNA or SNAP23 siRNA, followed by exposure to C. parvum infection for 24 h. Exosomes released into the apical supernatants were isolated and quantified. (B) and (C) TLR4-dependent induction of SNAP23 expression and its phosphorylation in cells following C. parvum infection, as assessed by Western blot (B) and immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis (C). C. parvum infection increased total and phosphorylated SNAP23 levels in H69 cells, but not in cells stably expressing TLR4-DN. (D) C. parvum infection enhances direct interactions between SNAP23 and IKK2. H69 cells were exposed to C. parvum for 24 h, and direct interaction between SNAP23 and IKK2 was measured by IP. * p<0.05 ANOVA versus infected non-specific siRNA control.