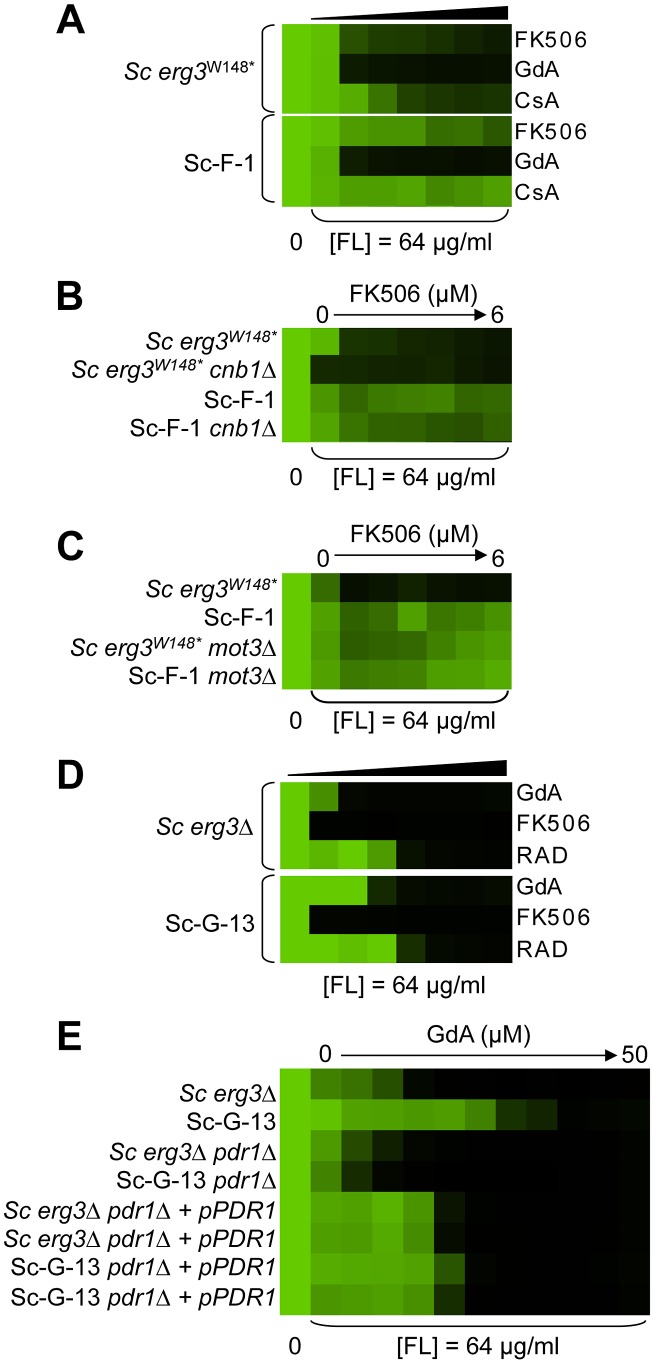
Figure 6. Whole-genome sequencing identifies mutations that confer resistance to azole and FK506, as well as azole and geldanamycin.
(A) Sc-F-1 is resistant to azole and FK506 and cross-resistant to azole and cyclosporin A. (B) Resistance of Sc-F-1 is calcineurin-independent. Deletion of CNB1, which encodes the regulatory subunit of calcineurin required for its activation, does not affect resistance of Sc-F-1. (C) Deletion of MOT3 in the ancestral strain confers resistance to azole and FK506 equivalent to Sc-F-1, which is consistent with the MOT3G265* allele of Sc-F-1 conferring resistance to azole and FK506. (D) Sc-G-13 is slightly resistant to azole and geldanamycin. (E) Resistance to azole and geldanamycin in Sc-G-13 is reduced when PDRP865R is deleted and PDR1 is expressed on a plasmid. Resistance assays were performed and analyzed as in Figure 2, with incubation for 2 days at 30°C in YPD (A–D) or SD (E). CsA = cyclosporin A; GdA = geldanamycin; RAD = radicicol; and FL = fluconazole.