Abstract
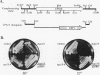
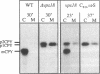
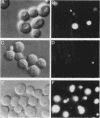
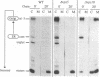
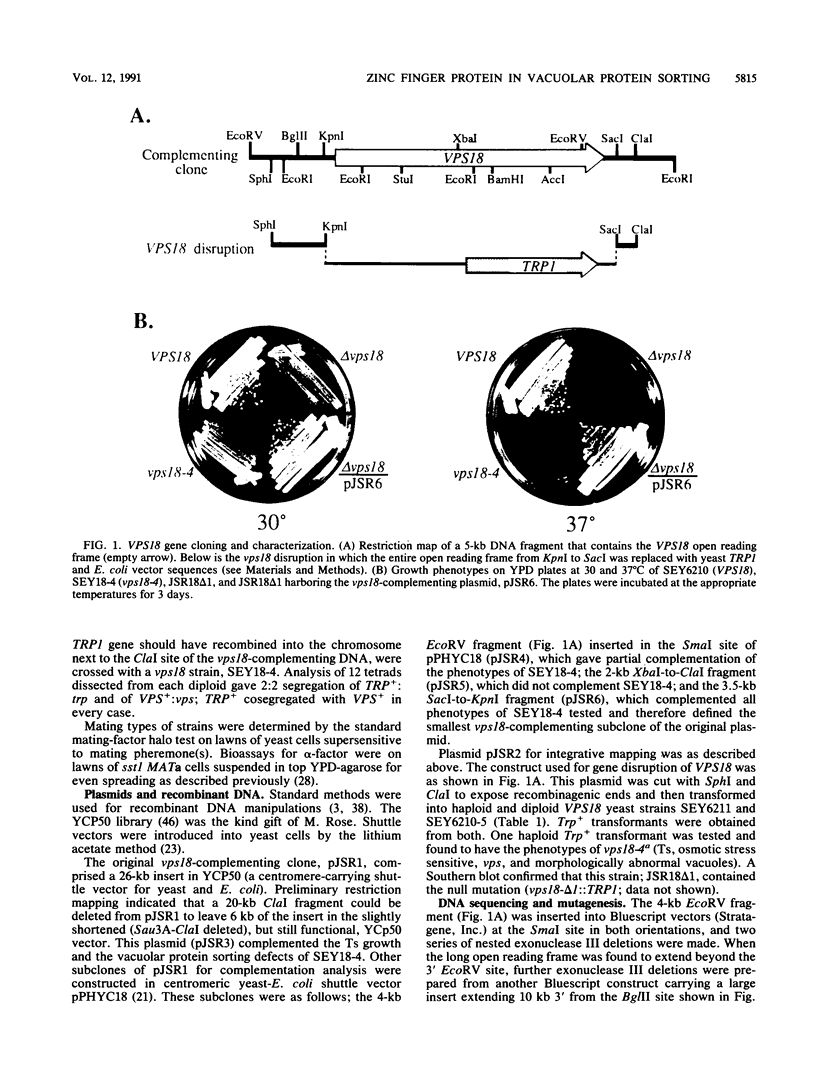
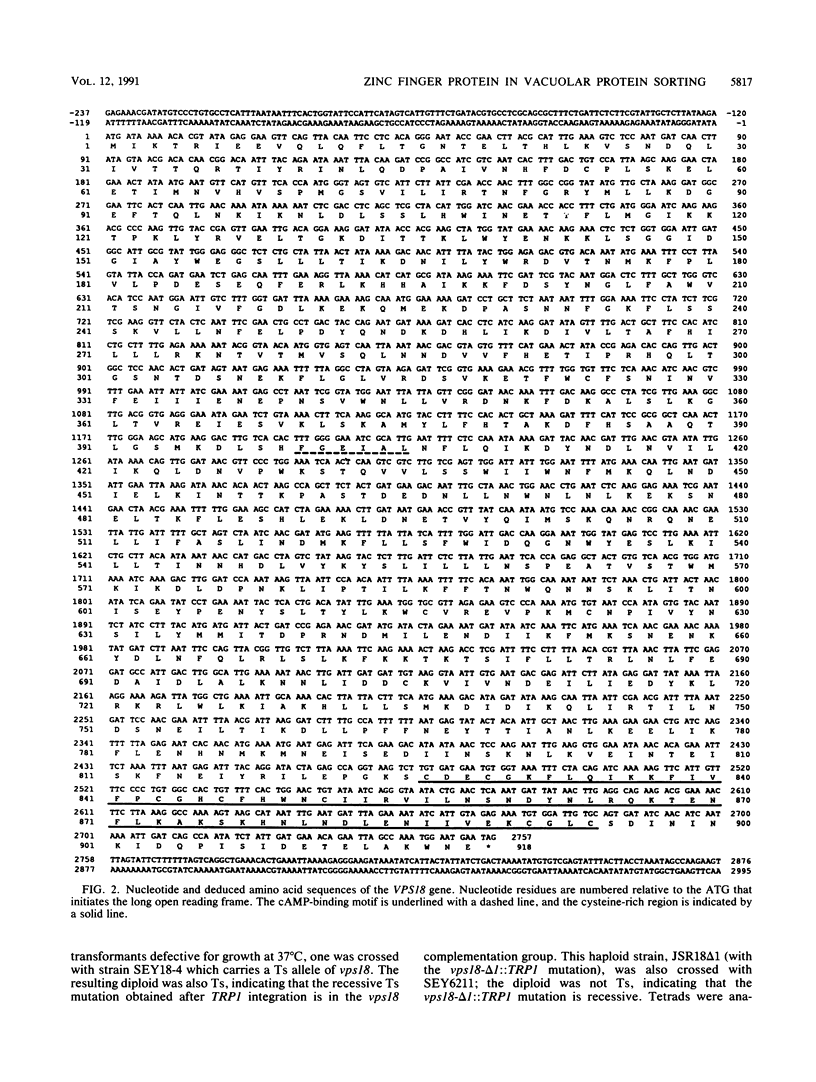
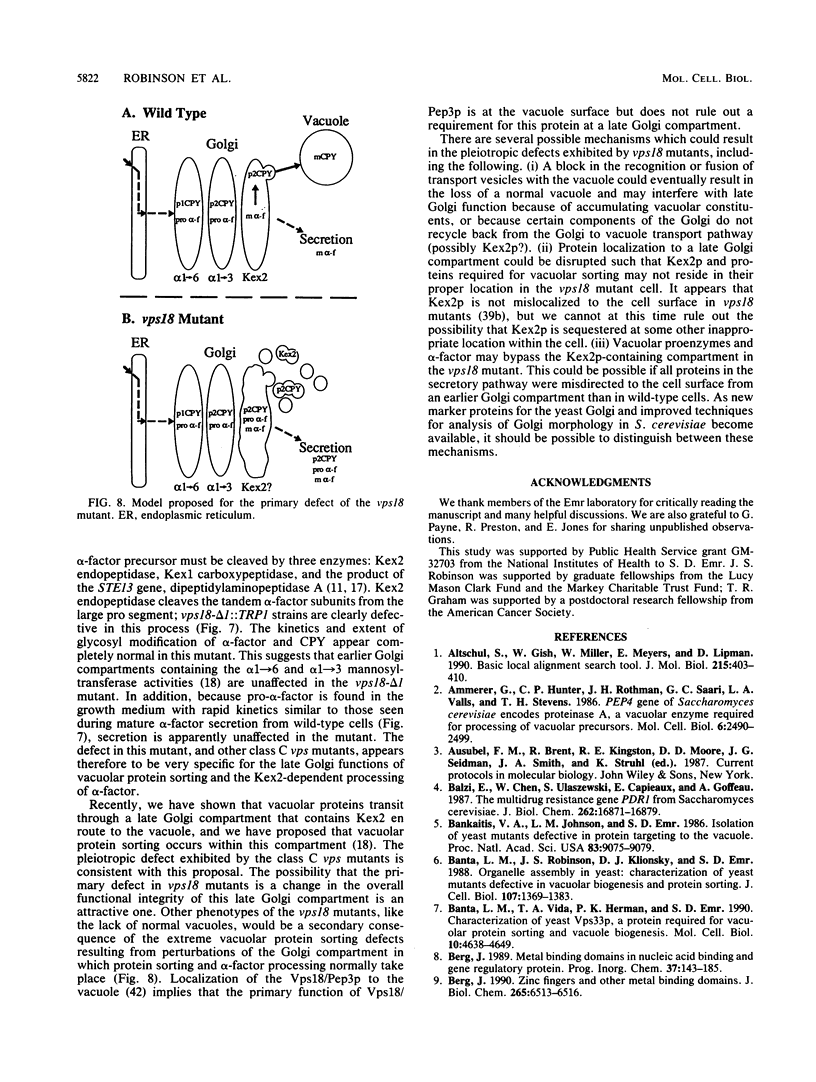
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains carrying vps18 mutations are defective in the sorting and transport of vacuolar enzymes. The precursor forms of these proteins are missorted and secreted from the mutant cells. Most vps18 mutants are temperature sensitive for growth and are defective in vacuole biogenesis; no structure resembling a normal vacuole is seen. A plasmid complementing the temperature-sensitive growth defect of strains carrying the vps18-4 allele was isolated from a centromere-based yeast genomic library. Integrative mapping experiments indicated that the 26-kb insert in this plasmid was derived from the VPS18 locus. A 4-kb minimal complementing fragment contains a single long open reading frame predicted to encode a 918-amino-acid hydrophilic protein. Comparison of the VPS18 sequence with the PEP3 sequence reported in the accompanying paper (R. A. Preston, H. F. Manolson, K. Becherer, E. Weidenhammer, D. Kirkpatrick, R. Wright, and E. W. Jones, Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:5801-5812, 1991) shows that the two genes are identical. Disruption of the VPS18/PEP3 gene (vps18 delta 1::TRP1) is not lethal but results in the same vacuolar protein sorting and growth defects exhibited by the original temperature-sensitive vps18 alleles. In addition, vps18 delta 1::TRP1 MAT alpha strains exhibit a defect in the Kex2p-dependent processing of the secreted pheromone alpha-factor. This finding suggests that vps18 mutations alter the function of a late Golgi compartment which contains Kex2p and in which vacuolar proteins are thought to be sorted from proteins destined for the cell surface. The Vps18p sequence contains a cysteine-rich, zinc finger-like motif at the COOH terminus. A mutant in which the first cysteine of this motif was changed to serine results in a temperature-conditional carboxypeptidase Y sorting defect shortly after a shift to nonpermissive conditions. We identified a similar cysteine-rich motif near the COOH terminus of another Vps protein, the Vps11/Pep5/End1 protein. Preston et al. (Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:5801-5812, 1991) present evidence that the Vps18/Pep3 protein colocalizes with the Vps11/Pep5 protein to the cytosolic face of the vacuolar membrane. Together with the similar phenotypes exhibited by both vps11 and vps18 mutants, this finding suggests that they may function at a common step during vacuolar protein sorting and that the integrity of their zinc finger motifs may be required for this function.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammerer G., Hunter C. P., Rothman J. H., Saari G. C., Valls L. A., Stevens T. H. PEP4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes proteinase A, a vacuolar enzyme required for processing of vacuolar precursors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2490–2499. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzi E., Chen W., Ulaszewski S., Capieaux E., Goffeau A. The multidrug resistance gene PDR1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16871–16879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Johnson L. M., Emr S. D. Isolation of yeast mutants defective in protein targeting to the vacuole. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9075–9079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banta L. M., Robinson J. S., Klionsky D. J., Emr S. D. Organelle assembly in yeast: characterization of yeast mutants defective in vacuolar biogenesis and protein sorting. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1369–1383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banta L. M., Vida T. A., Herman P. K., Emr S. D. Characterization of yeast Vps33p, a protein required for vacuolar protein sorting and vacuole biogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4638–4649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Zinc fingers and other metal-binding domains. Elements for interactions between macromolecules. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6513–6516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H. Proteases and the processing of precursors to secreted proteins in yeast. Yeast. 1988 Mar;4(1):17–26. doi: 10.1002/yea.320040103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Melnick L. M., Blair L. C., Thorner J. Extracellular suppression allows mating by pheromone-deficient sterile mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):903–906. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.903-906.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmochowska A., Dignard D., Henning D., Thomas D. Y., Bussey H. Yeast KEX1 gene encodes a putative protease with a carboxypeptidase B-like function involved in killer toxin and alpha-factor precursor processing. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Riezman H. Characterization of the END1 gene required for vacuole biogenesis and gluconeogenic growth of budding yeast. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1349–1359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03515.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Ozkaynak E., Varshavsky A. The yeast polyubiquitin gene is essential for resistance to high temperatures, starvation, and other stresses. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90711-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C. Expression of RNA transcripts for the postsynaptic 43 kDa protein in innervated and denervated rat skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80629-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A. J., Thorner J. Intracellular targeting and structural conservation of a prohormone-processing endoprotease. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):482–486. doi: 10.1126/science.2683070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Enzymes required for yeast prohormone processing. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:345–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham T. R., Emr S. D. Compartmental organization of Golgi-specific protein modification and vacuolar protein sorting events defined in a yeast sec18 (NSF) mutant. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):207–218. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarer B. K., Lillie S. H., Adams A. E., Magdolen V., Bandlow W., Brown S. S. Purification of profilin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and analysis of profilin-deficient cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):105–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Tanner W. Biosynthesis of the vacuolar yeast glycoprotein carboxypeptidase Y. Conversion of precursor into the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):599–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman P. K., Emr S. D. Characterization of VPS34, a gene required for vacuolar protein sorting and vacuole segregation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6742–6754. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman P. K., Stack J. H., DeModena J. A., Emr S. D. A novel protein kinase homolog essential for protein sorting to the yeast lysosome-like vacuole. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90650-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. Genetic evidence that zinc is an essential co-factor in the DNA binding domain of GAL4 protein. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):353–355. doi: 10.1038/328353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. W. Proteinase mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1977 Jan;85(1):23–33. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. W. The synthesis and function of proteases in Saccharomyces: genetic approaches. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:233–270. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Blair L., Brake A., Sprague G., Thorner J. Yeast alpha factor is processed from a larger precursor polypeptide: the essential role of a membrane-bound dipeptidyl aminopeptidase. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):839–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Brake A., Blair L., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. Isolation of the putative structural gene for the lysine-arginine-cleaving endopeptidase required for processing of yeast prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1075–1089. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klionsky D. J., Banta L. M., Emr S. D. Intracellular sorting and processing of a yeast vacuolar hydrolase: proteinase A propeptide contains vacuolar targeting information. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2105–2116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klionsky D. J., Emr S. D. Membrane protein sorting: biosynthesis, transport and processing of yeast vacuolar alkaline phosphatase. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2241–2250. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08348.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klionsky D. J., Herman P. K., Emr S. D. The fungal vacuole: composition, function, and biogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Sep;54(3):266–292. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.3.266-292.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladjimi M. M., Kantrowitz E. R. Catalytic-regulatory subunit interactions and allosteric effects in aspartate transcarbamylase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):312–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):260–267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Hasson T. B., Hasson M. S., Schekman R. Genetic and biochemical characterization of clathrin-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3888–3898. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston R. A., Manolson M. F., Becherer K., Weidenhammer E., Kirkpatrick D., Wright R., Jones E. W. Isolation and characterization of PEP3, a gene required for vacuolar biogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5801–5812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Preston R. A., Adams A. E., Stearns T., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K., Jones E. W. Fluorescence microscopy methods for yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:357–435. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61620-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond C. K., O'Hara P. J., Eichinger G., Rothman J. H., Stevens T. H. Molecular analysis of the yeast VPS3 gene and the role of its product in vacuolar protein sorting and vacuolar segregation during the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):877–892. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. S., Klionsky D. J., Banta L. M., Emr S. D. Protein sorting in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation of mutants defective in the delivery and processing of multiple vacuolar hydrolases. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4936–4948. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. H., Howald I., Stevens T. H. Characterization of genes required for protein sorting and vacuolar function in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2057–2065. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. H., Raymond C. K., Gilbert T., O'Hara P. J., Stevens T. H. A putative GTP binding protein homologous to interferon-inducible Mx proteins performs an essential function in yeast protein sorting. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1063–1074. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90070-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T., Esmon B., Schekman R. Early stages in the yeast secretory pathway are required for transport of carboxypeptidase Y to the vacuole. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichert U., Mechler B., Müller H., Wolf D. H. Lysosomal (vacuolar) proteinases of yeast are essential catalysts for protein degradation, differentiation, and cell survival. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16037–16045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford C. A., Dixon C. K., Manolson M. F., Wright R., Jones E. W. Isolation and characterization of PEP5, a gene essential for vacuolar biogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Aug;125(4):739–752. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.4.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Nomura M. Suppressor analysis of temperature-sensitive mutations of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase I in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a suppressor gene encodes the second-largest subunit of RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):754–764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]