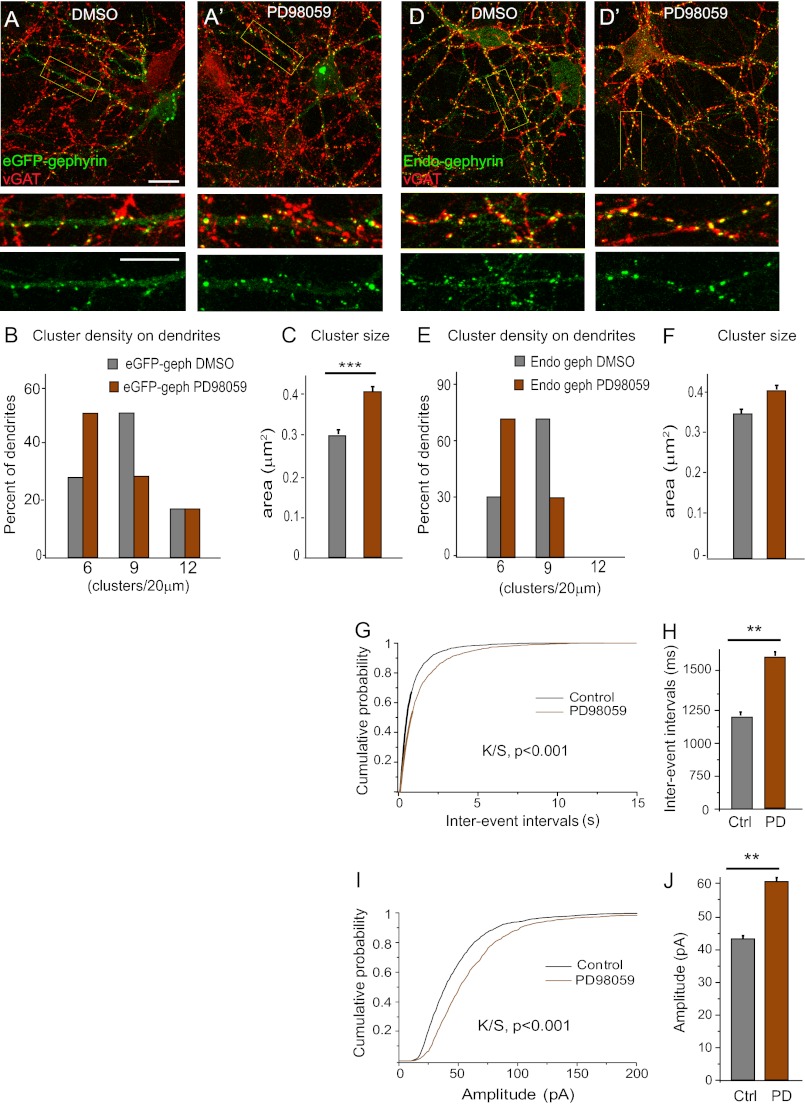
FIGURE 6.
Effects of short term ERK inhibition on gephyrin clustering and GABAergic mIPSC. A and A′, representative images of eGFP-gephyrin-transfected neurons (11 + 4 DIV) treated with either vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)) or ERK inhibitor PD98059 (25 μm) for 3 h before fixation and staining. Boxed areas are enlarged below the main picture to demonstrate postsynaptic localization of eGFP-gephyrin clusters (green) apposed tot VGAT-positive terminals (red). B and C, histograms of cluster density distribution and size, showing that short term blockade of ERK increases eGFP-gephyrin cluster size (means ± S.E.; ***, p < 0.001) but not density (see main text for statistics). D and D′, 15 DIV neurons treated with dimethyl sulfoxide or PD98059 for 3 h before fixation and staining for endogenous gephyrin (green) and GABAergic presynaptic terminals VGAT (red). E and F, quantification of endogenous gephyrin cluster density (normalized per 20-μm dendrite) revealed a significant decrease but no change in size (means ± S.E.; see main text for statistics). G–J, interevent intervals and amplitude of GABAergic mIPSC recorded in 15 DIV neurons following 3 h of exposure to dimethyl sulfoxide and PD98059. Cumulative probability distribution analysis revealed significantly increased interevent intervals and amplitude, as depicted also with histograms (means ± S.E.; **, p < 0.01; see Table 2 for statistical analysis). Scale bars: A and D, 10 μm. Ctrl, control; PD, PD98059.