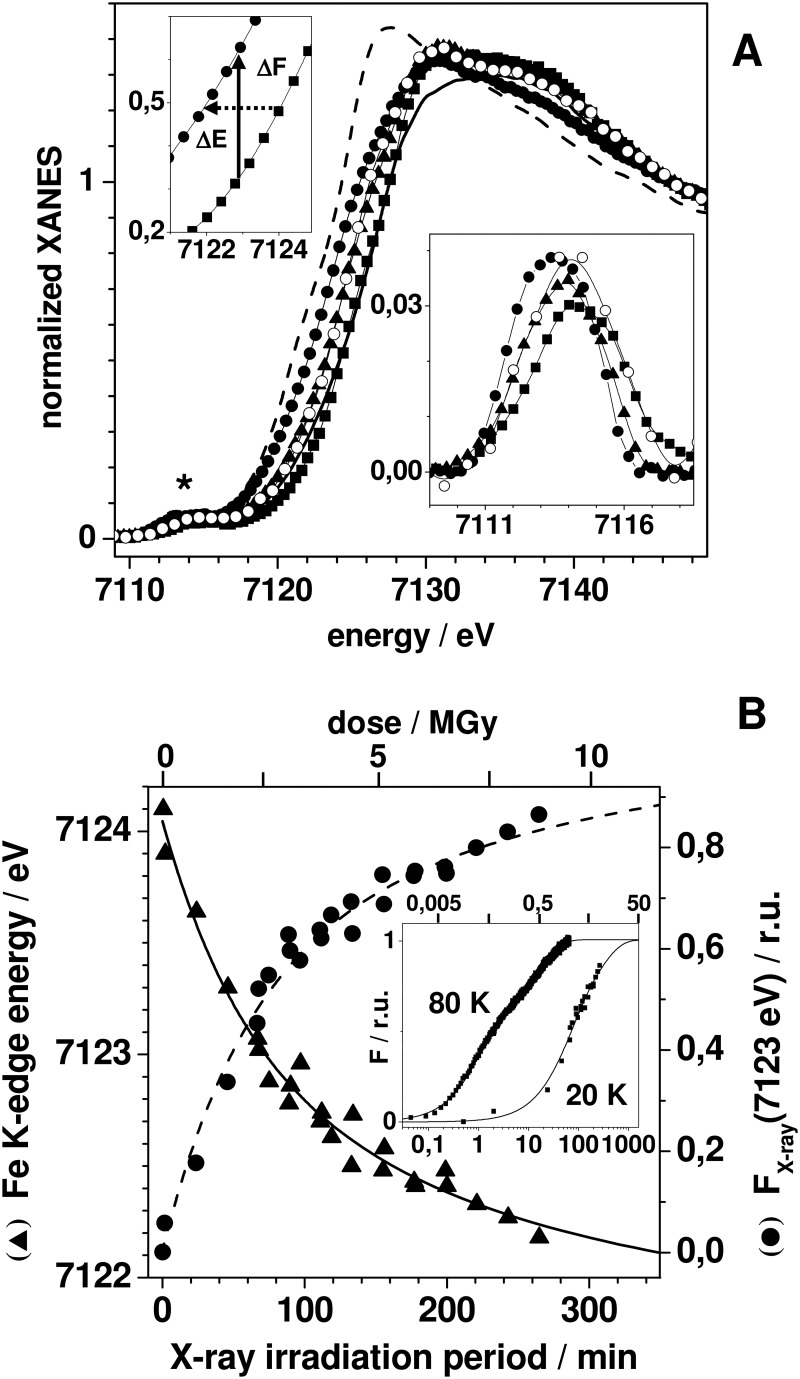
FIGURE 2.
XPR kinetics of the FeFe cofactor. A, iron XANES spectra of CtR2FeFeox (squares) and CtR2FeFered (open circles) of CtR2FeFe samples initially in the oxidized (ox) state after x-ray exposure at 20 K for ∼90 min (triangles) and ∼260 min (solid circles), and of iron oxidation state references (FeIIN4O2, dashed line; FeIIIN5O, solid line; see Table 3). Upper inset, K-edge spectra around the 50% level of CtR2FeFeox and CtR2FeFex260, the arrows mark the edge downshift (ΔE) and corresponding fluorescence intensity increase (ΔF) for an excitation energy of 7123 eV. Lower inset, expanded view of isolated pre-edge peaks in the XANES (asterisk). B, K-edge energies (triangles, left y axis) and x-ray fluorescence intensities at 7123 eV (circles, right y axis) at 20 K, together with the fit curves calculated using parameters in Table 3. Inset, time scan trace of the x-ray fluorescence intensity at 7123 eV at 80 K, K-edge data at 20 K, and fit curves (Table 3) on a logarithmic axis. Traces were normalized to unity amplitude after offset subtraction on the basis of the fit results. The given dose values (in Gy, gray = J kg−1) are approximate and correspond to the incident dose, the absorbed dose in 1 mm of water for an energy of 7125 eV is ∼77% of the incident dose. Dose values were calculated for an energy of 7125 eV = 1.14 × 10−14 joule, a flux (upper limit) of 1011 photons s−1, and an irradiated volume of 0.2 mm3 corresponding to 2.15 × 10−7 kg (aqueous buffer plus R2 protein contributing about 0.15 × 10−7 kg at 1.8 mm and a molecular mass of ∼43 kDa).