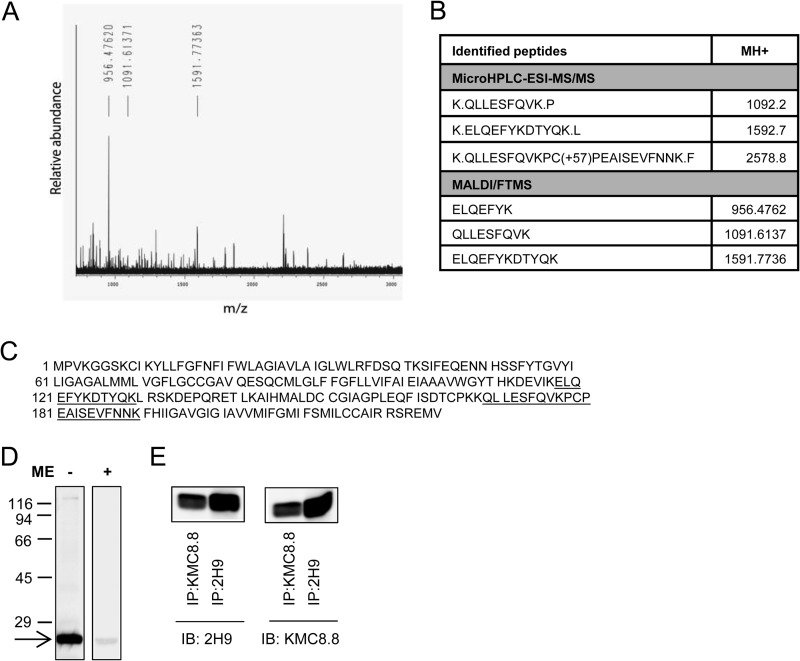
FIGURE 2.
Identification of CD9 as the target protein of 2H9 mAb. 2H9 mAb covalently bound to protein G resin by dimethylpimelimidate was used to pulldown the target Ag from postnuclear supernatant of BMMCs lysed in a lysis buffer containing 1% Triton X-100. Bound material was eluted from the resin by SDS-PAGE sample buffer, size-fractionated on 12% SDS-PAGE, and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. The major band was excised and analyzed with HPLC in combination with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (microHPLC-ESI-MS/MS) and MALDI-Fourier transform mass spectrometry (MALDI/FTMS). A, the chart represents the spectrum of detected peptides from trypsin-digested immunoprecipitated protein. Masses of identified peptides (MH+) and their corresponding peaks are indicated. B, table shows sequences identified by MS analysis with mass of their appropriate MH+ ions. C, positions of the identified sequences (underlined) in the whole CD9 protein (NCBI Reference Sequence NP_031683.1). D, lysates from BMMCs were diluted with SDS-PAGE sample buffer supplemented with (+) or without (−) 2-mercaptoethanol (ME), size fractionated by SDS-PAGE, and analyzed by immunoblotting with 2H9 mAb followed by anti-rat IgG HRP conjugate. The arrow indicates the migration of the 2H9 target protein and numbers on the left represent the position of the molecular mass markers in kDa. E, BMMCs were lysed as in A and postnuclear supernatants were immunoprecipitated (IP) with 2H9 or KMC8.8 antibodies immobilized to protein G resin. Material released from the resin was fractionated on a 12% SDS-PAGE gel and analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with 2H9 or KMC8.8 Abs. The data presented in D and E are typical results from at least 3 experiments performed.