Figure 3.
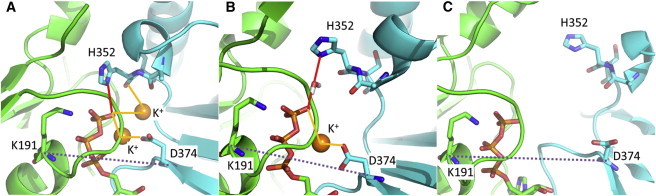
Effects of K+ on the stability of the ATP-γ-phosphate binding site. The final structures of the ATP-γ-phosphate binding site in the first runs of simulations K2NATPIM (A), K1NATPIM (B), and K0NATPIM (C) are shown. The dashed line indicates the distance between the Cα atoms of D374 and K191 that is used as an indicator of the opening of the interface. In panel A, a hydrogen bond between H352 and the γ-phosphate is shown with the red line, and interactions involving K+ ions are shown in yellow lines. In simulations containing two K+ ions, the ATP-binding site was tight. In the case of one K+ ion, the side chain of H352 formed a water-mediated hydrogen bond with the γ-phosphate. In contrast, the K+-free simulation exhibited a large opening motion at the ATP-binding site.
