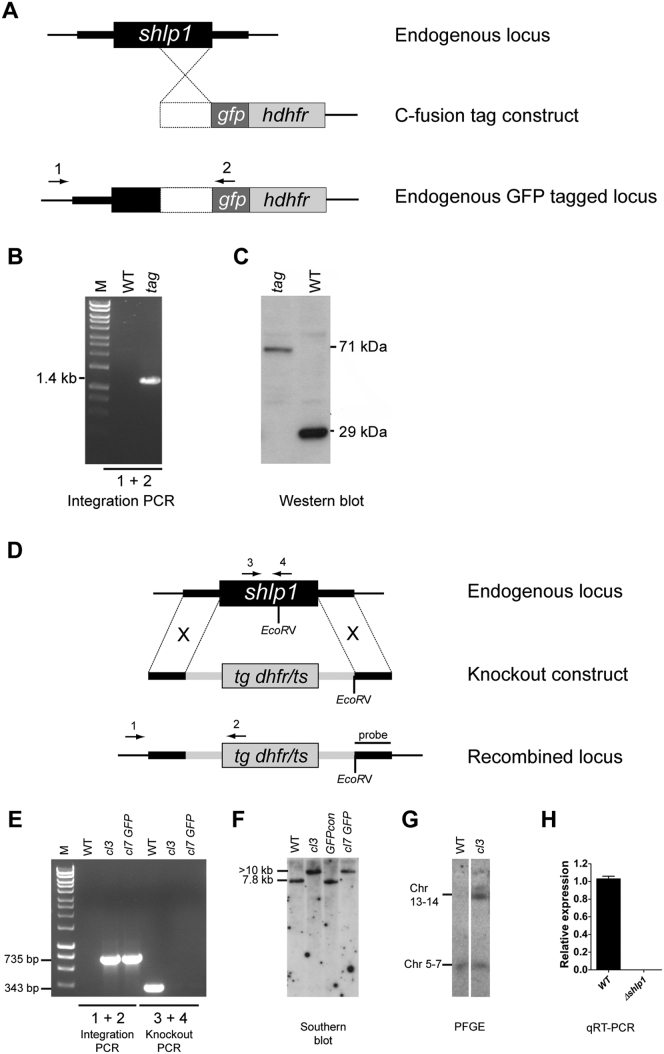
Figure S2.
gfp Tagging of the Endogenous shlp1 Locus and Knockout of shlp1, Related to Figure 3
(A) Schematic representation of the gene targeting strategy used for gene tagging the endogenous locus with gfp via single homologous recombination. The C-fusion tag construct contains an insert (white box) homologous to the 3′ end of the shlp1 ORF fused to gfp. A human dehydrofolate reductase selectable marker (hdhfr) allows for selection of transgenic parasites. Arrows 1 and 2 indicate primers used for diagnostic PCR.
(B) Diagnostic integration PCR showing the expected 1.4 kb band and confirming successful integration of the tagging construct.
(C) Western blot analysis using an anti-GFP (Invitrogen) antibody against protein extracted from gametocytes of WT P. berghei ANKA 507 clone 1 constitutively expressing GFP (wt) and transgenic (tag) parasites showing bands of expected sizes of 29 kDa for wild-type-GFP and 71 kDa for SHLP1-GFP.
(D) Schematic representation of the endogenous shlp1 locus, the knockout construct and the recombined shlp1 locus following double cross-over recombination. The knockout construct contains a Toxoplasma gondii dehydrofolate reductase/thymidylate synthase (tg dhfr/ts) cassette with a Pbdhfr 3′ UTR for selection of transgenic parasites with pyrimethamine. Arrows 1, 2, 3 and 4 indicate binding sites for primers used in integration PCR and knockout PCR. EcoRV restriction sites and probe binding sites used for Southern blot analysis are shown.
(E) Genotypic analysis by integration PCR and knockout PCR. Presence of a 735 bp band using integration specific primers 1 and 2 on gDNA of Δshlp1 mutants cl3 and cl7 GFP generated in 507 clone 1 indicates correct integration of the knockout construct. Absence of the 343 bp WT specific band amplified by primers 3 and 4 in both mutants shows loss of the wild-type shlp1 locus. WT gDNA was used as control.
(F) Genotypic analysis by Southern blot. gDNA of WT parasites, wild-type 507 clone 1 (GFPcon) and Δshlp1 mutants cl3 and cl7 GFP was analyzed by Southern blot following EcoRV digestion. A probe homologous to the shlp1 3′UTR recognizes a 7.8 kb fragment for the endogenous locus and a > 10 kb fragment for the recombined locus.
(G) Pulse-field gel electrophoresis blot (PFGE) hybridized with a Pbdhfr 3′UTR probe. The probe hybridizes to the endogenous dhfr locus on chromosome 7 and the disrupted locus on chromosome 14. (H) Bar graph showing relative expression of endogenous shlp1 in Δshlp1 mutants using qRT-PCR compared to wild-type. Error bars represent ±SEM, n = 3 from three separate experiments in both clone 3 and clone 7 GFP.