Figure 8.
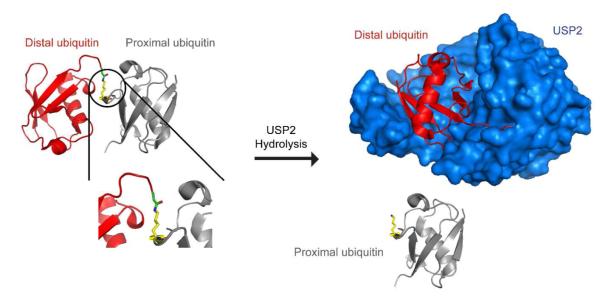
Illustration of the proximal and distal ubiquitin in USP2-catalyzed deubiquitination. Before USP2-catalyzed hydrolysis of diubiquitin, the C-terminal carboxylate of the distal ubiquitin (red) is covalently linked to the side-chain amino group of a lysine 48 residue of the proximal ubiquitin (grey) by an isopeptide bond. The C-terminal carboxylate of the distal ubiquitin becomes covalently bound to the USP2 (blue) active site cysteine residue forming a thioester intermediate. Then a deacylation step occurs followed by release of distal ubiquitin. This illustration was generated using the X-ray crystal structure of a Lys48-linked diubiquitin with an open conformation (17) and the cocrystal structure of USP2 in complex with ubiquitin (30).
