Fig. 7.
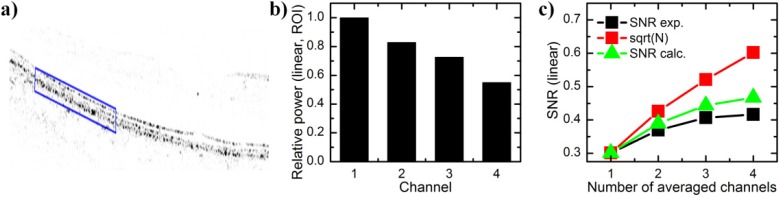
a) Retinal image with inverse contrast and in linear power scale (FFT signal squared). Blue box indicated region of interest (ROI) around the RPE layer. b) Mean signal power in the ROI with respect to the power in the active channel 1. c) Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) calculated as power mean to power standard deviation over the entire image (black squares). Since the signal is weaker in the passive channels, the SNR increase is lower than with the square root of channel number (black squares). The experimental SNR increase is close to the calculated value (green triangles), which takes into account the varying power levels, assuming completely uncorrelated speckle patterns (Eq. (1)).
