Abstract
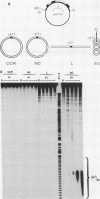
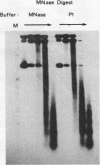
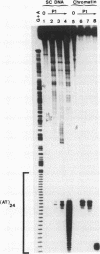
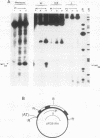
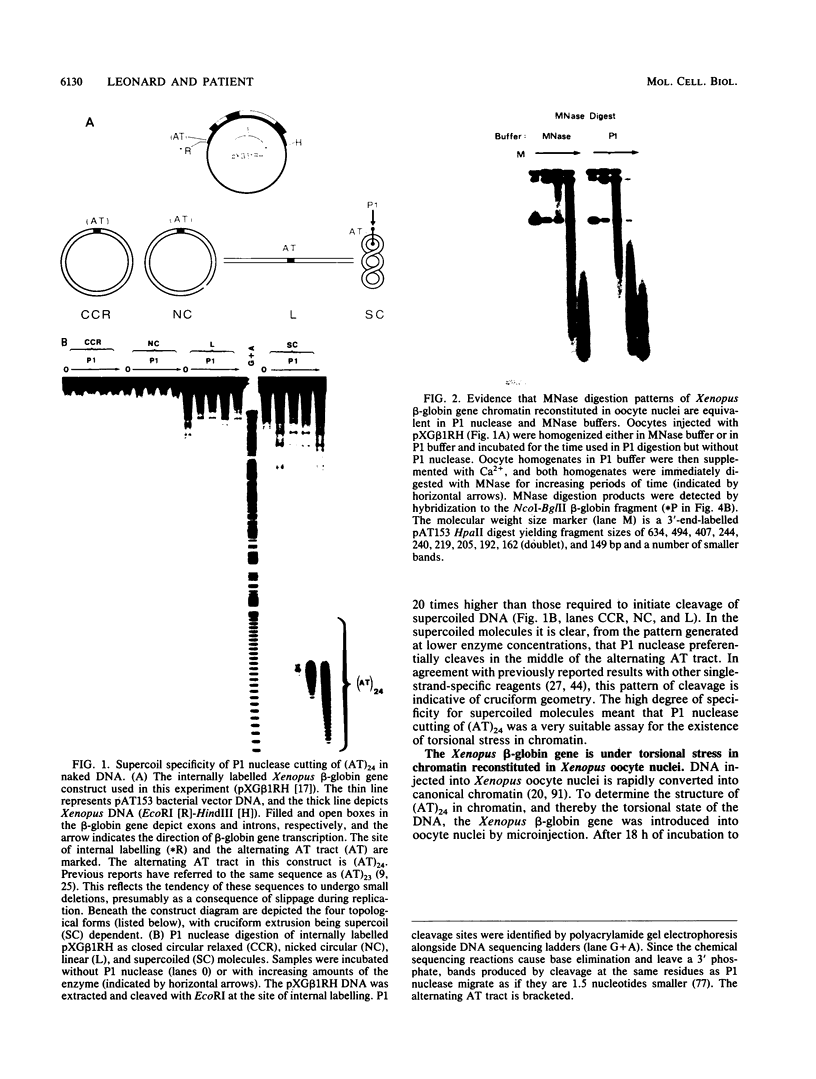
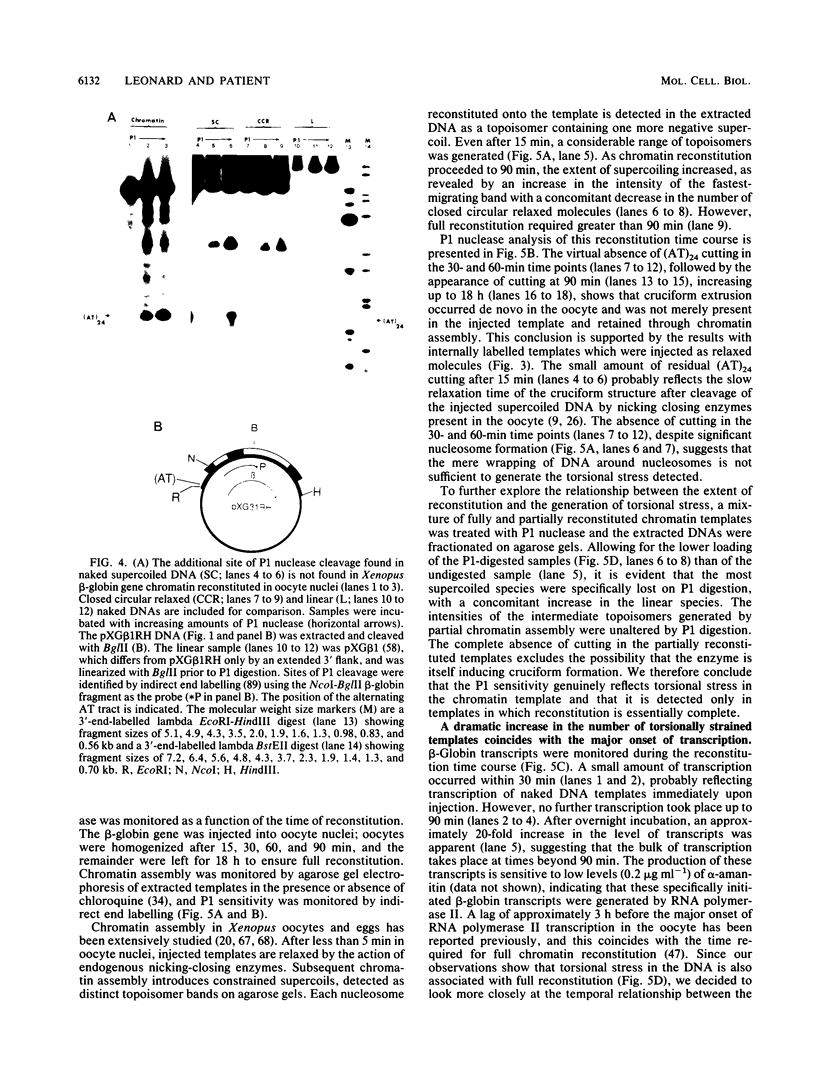
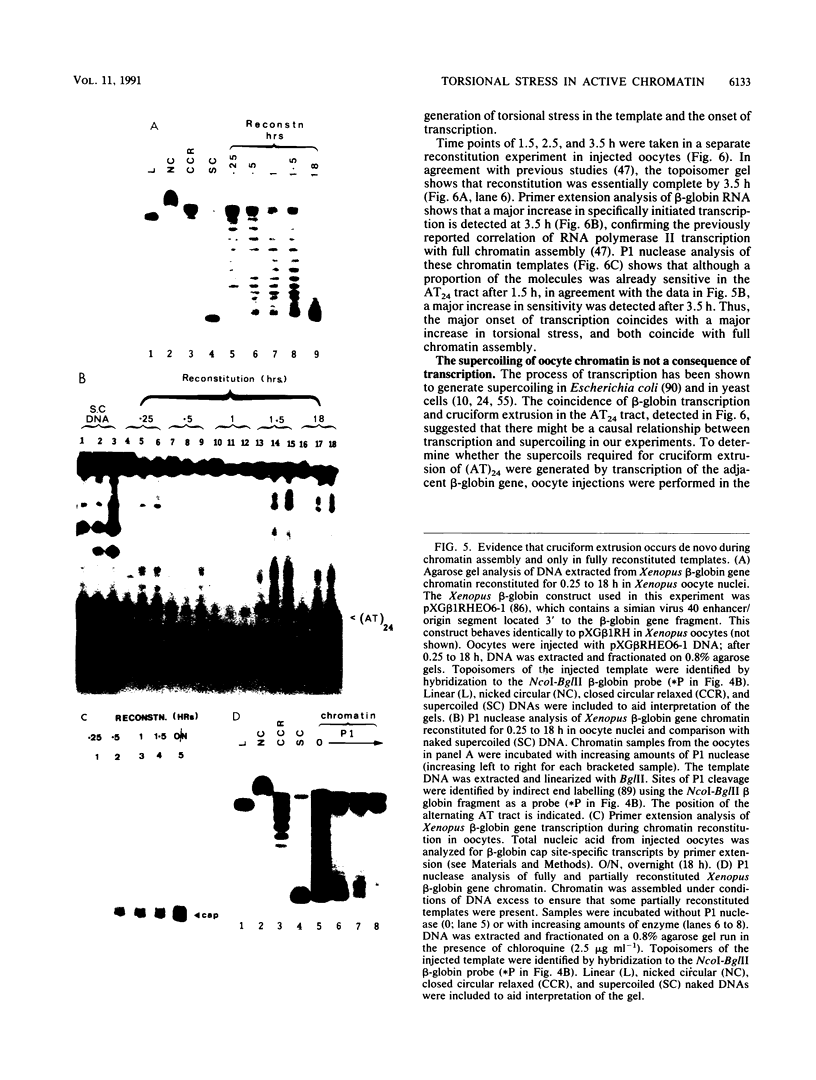
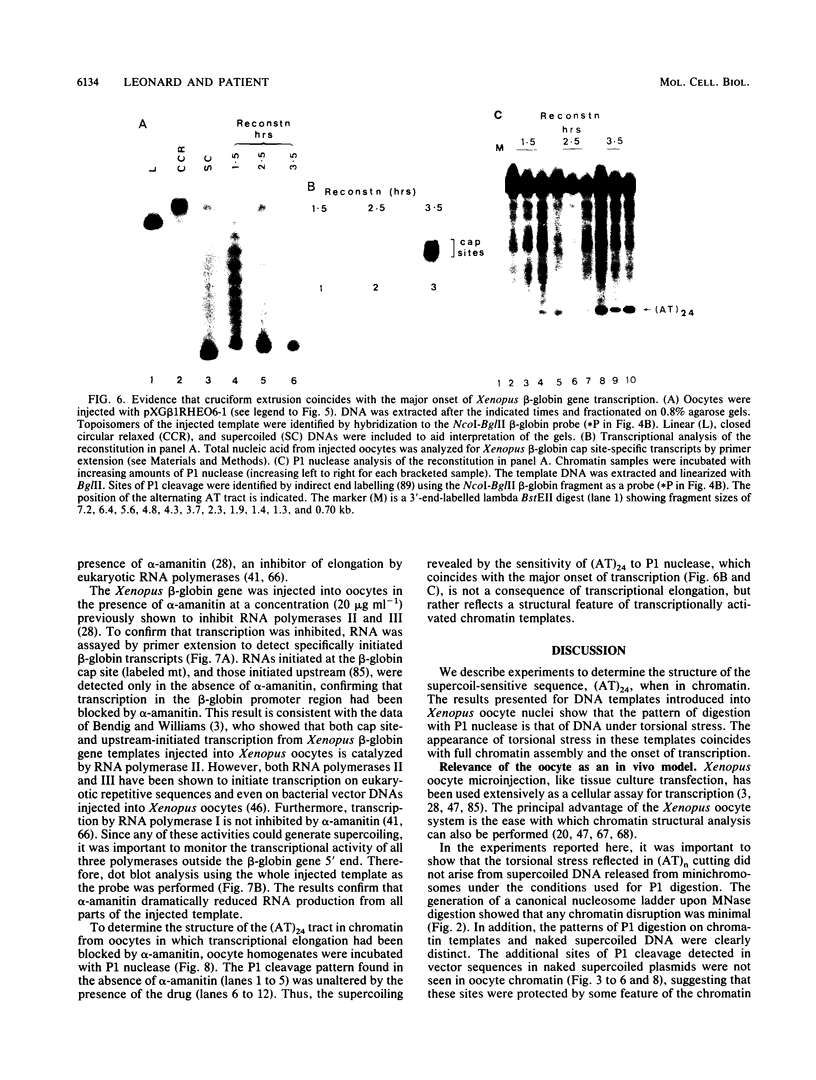
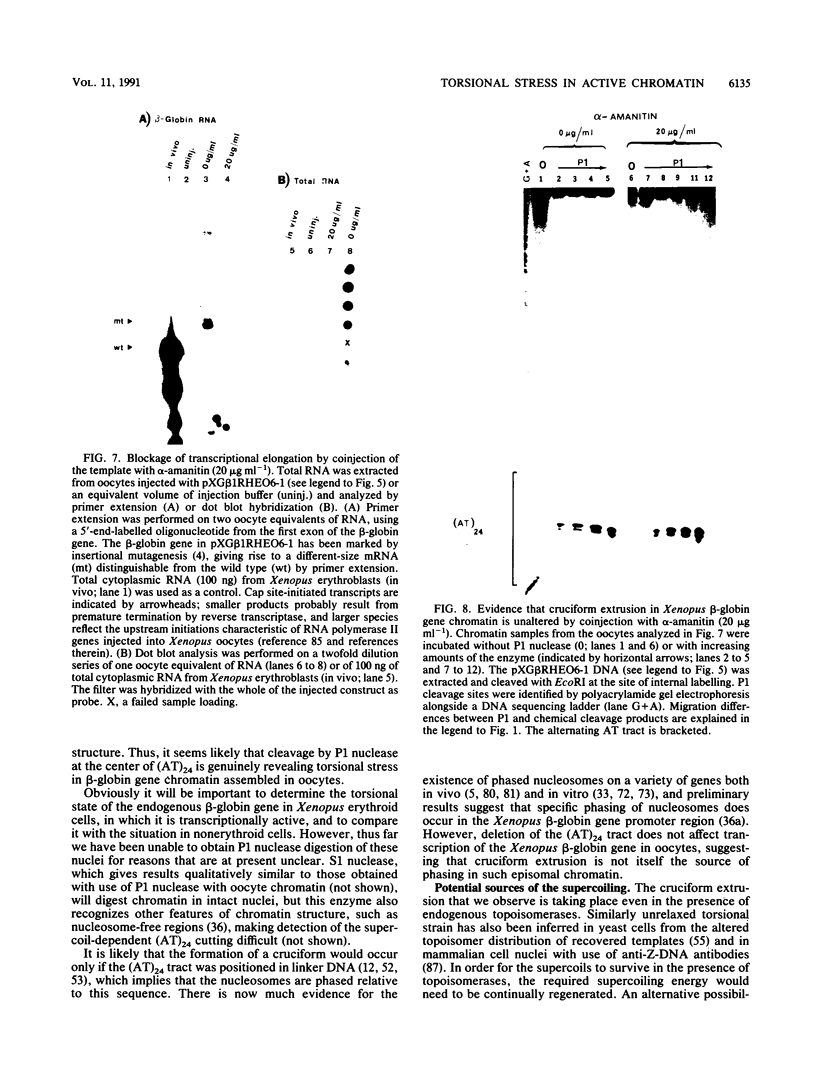
The existence of torsional stress in eukaryotic chromatin has been controversial. To determine whether it could be detected, we probed the structure of an alternating AT tract. These sequences adopt cruciform geometry when the DNA helix is torsionally strained by negative supercoiling. The single-strand-specific nuclease P1 was used to determine the structure of an alternating AT sequence upstream of the Xenopus beta-globin gene when assembled into chromatin in microinjected Xenopus oocytes. The pattern of cleavage by P1 nuclease strongly suggests that the DNA in this chromatin template is under torsional stress. The cruciform was detected specifically in the most fully reconstituted templates at later stages of chromatin assembly, suggesting that negative supercoiling is associated with chromatin maturation. Furthermore, the number of torsionally strained templates increased dramatically at the time when transcription of assembled chromatin templates began. Transcription itself has been shown to induce supercoiling, but the requisite negative supercoiling for cruciform extrusion by (AT)n in oocytes was not generated in this way since the characteristic P1 cutting pattern was retained even when RNA polymerase elongation was blocked with alpha-amanitin. Thus, torsional stress is associated with transcriptional activation of chromatin templates in the absence of ongoing transcription.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almouzni G., Méchali M. Assembly of spaced chromatin involvement of ATP and DNA topoisomerase activity. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4355–4365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur C. P., Knippers R. Protein-induced bending of the simian virus 40 origin of replication. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):1009–1019. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendig M. M., Williams J. G. Differential expression of the Xenopus laevis tadpole and adult beta-globin genes when injected into fertilized Xenopus laevis eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):567–570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendig M. M., Williams J. G. Fidelity of transcription of Xenopus laevis globin genes injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes and unfertilized eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2109–2119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Cantor C. R., Axel R. Nucleosomes are phased along the mouse beta-major globin gene in erythroid and nonerythroid cells. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90835-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E., Beltrame M., Paonessa G. Specific recognition of cruciform DNA by nuclear protein HMG1. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2922595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E. Interaction of a protein from rat liver nuclei with cruciform DNA. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):843–849. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer A. C., Enver T., Greaves D. R., Allan J., Patient R. K. 5' structural motifs and Xenopus beta globin gene activation. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 20;199(4):575–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90302-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Sternglanz R. Transcription-dependent DNA supercoiling in yeast DNA topoisomerase mutants. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Pettijohn D. E. Interaction of the Escherichia coli HU protein with DNA. Evidence for formation of nucleosome-like structures with altered DNA helical pitch. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90405-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffarelli E., Leoni L., Sampaolese B., Savino M. Persistence of cruciform structure and preferential location of nucleosomes on some regions of pBR322 and ColE 1 DNAs. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 15;156(2):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. A., Allfrey V. G. Rapid and reversible changes in nucleosome structure accompany the activation, repression, and superinduction of murine fibroblast protooncogenes c-fos and c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Halligan B., Cooke C. A., Heck M. M., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase II is a structural component of mitotic chromosome scaffolds. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1706–1715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Heck M. M. Localization of topoisomerase II in mitotic chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1716–1725. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elborough K. M., West S. C. Specific binding of cruciform DNA structures by a protein from human extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3603–3616. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enver T., Brewer A. C., Patient R. K. Role for DNA replication in beta-globin gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1301–1308. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler R. F., Skinner D. M. Eukaryotic DNA diverges at a long and complex pyrimidine.purine tract that can adopt altered conformations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8994–9001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargiulo G., Worcel A. Analysis of the chromatin assembled in germinal vesicles of Xenopus oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 5;170(3):699–722. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Felsenfeld G., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. Effects of DNA supercoiling on the topological properties of nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2620–2623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laroche T., Falquet J., Boy de la Tour E., Laemmli U. K. Metaphase chromosome structure. Involvement of topoisomerase II. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):613–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Tomizawa J. DNA gyrase and DNA supercoiling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever G. N., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of intracellular DNA can occur in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):849–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Patient R. K. (AT)n is an interspersed repeat in the Xenopus genome. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2617–2626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Patient R. K., Lilley D. M. Facile cruciform formation by an (A-T)34 sequence from a Xenopus globin gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):461–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Patient R. K. RecBC, sbcB independent, (AT)n-mediated deletion of sequences flanking a Xenopus laevis beta globin gene on propagation in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4147–4158. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Melton D. A. Gene transfer in amphibian eggs and oocytes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:189–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Taylor A., Kedes L. DNA bending is induced by a transcription factor that interacts with the human c-FOS and alpha-actin promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2162–2166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Transition of a cloned d(AT)n-d(AT)n tract to a cruciform in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4343–4363. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Klysik J., Wells R. D. Influence of DNA sequence on the formation of non-B right-handed helices in oligopurine.oligopyrimidine inserts in plasmids. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7386–7396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):263–265. doi: 10.1038/285263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalas P., Gray F. C., Allan J. Precise nucleosome positioning in the promoter of the chicken beta A globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):501–517. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancillotti F., Lopez M. C., Arias P., Alonso C. Z-DNA in transcriptionally active chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1560–1564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. D., Laemmli U. K. Higher order metaphase chromosome structure: evidence for metalloprotein interactions. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. DNA opens up--supercoiling and heavy breathing. Trends Genet. 1988 Apr;4(4):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan J. A., Lilley D. M. A two-state conformational equilibrium for alternating (A-T)n sequences in negatively supercoiled DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 20;197(4):707–721. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90477-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan J. A., Palecek E., Lilley D. M. (A-T)n tracts embedded in random sequence DNA--formation of a structure which is chemically reactive and torsionally deformable. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9291–9309. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli T., Prives C. pBR322 DNA inhibits simian virus 40 gene expression in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1579–1594. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. J., Mertz J. E. Template structural requirements for transcription in vivo by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Mizuuchi M., Gellert M. Cruciform structures in palindromic DNA are favored by DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse R. H., Cantor C. R. Nucleosome core particles suppress the thermal untwisting of core DNA and adjacent linker DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4653–4657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse R. H., Pederson D. S., Dean A., Simpson R. T. Yeast nucleosomes allow thermal untwisting of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10311–10330. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Pienta K. J., Barrack E. R., Coffey D. S. The role of the nuclear matrix in the organization and function of DNA. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:457–475. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J., Martin R. G. DNA stem-loop structures bind poorly to histone octamer cores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4669–4673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobile C., Nickol J., Martin R. G. Nucleosome phasing on a DNA fragment from the replication origin of simian virus 40 and rephasing upon cruciform formation of the DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2916–2922. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton V. G., Marvin K. W., Yau P., Bradbury E. M. Nucleosome linking number change controlled by acetylation of histones H3 and H4. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19848–19852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne B. I., Guarente L. Transcription by RNA polymerase II induces changes of DNA topology in yeast. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):766–772. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patient R. K., Allan J. Active chromatin. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;1(3):454–459. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patient R. K., Harris R., Walmsley M. E., Williams J. G. The complete nucleotide sequence of the major adult beta globin gene of Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8521–8523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. R., Laemmli U. K. The structure of histone-depleted metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):817–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Chalkley R. The effect of histone hyperacetylation on the nuclease sensitivity and the solubility of chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3313–3318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior C. P., Cantor C. R., Johnson E. M., Littau V. C., Allfrey V. G. Reversible changes in nucleosome structure and histone H3 accessibility in transcriptionally active and inactive states of rDNA chromatin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90561-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Drlica K. DNA supercoiling and prokaryotic transcription. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Manes S. H., Drlica K. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I mutants: increased supercoiling is corrected by mutations near gyrase genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90402-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Initiation of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase from supercoiled and non-supercoiled bacteriophage PM2 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 5;91(4):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90274-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. M., Higgins C. F., Lilley D. M. The genetic control of DNA supercoiling in Salmonella typhimurium. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1745–1752. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in Xenopus laevis. Isolation and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryoji M., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vivo studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryoji M., Worcel A. Structure of the two distinct types of minichromosomes that are assembled on DNA injected in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):923–932. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90352-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Moyne G., Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuey D. J., Parker C. S. Bending of promoter DNA on binding of heat shock transcription factor. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):459–461. doi: 10.1038/323459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U. RNA polymerase unwinds an 11-base pair segment of a phage T7 promoter. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):651–652. doi: 10.1038/279651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Stafford D. W. Structural features of a phased nucleosome core particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):51–55. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Thoma F., Brubaker J. M. Chromatin reconstituted from tandemly repeated cloned DNA fragments and core histones: a model system for study of higher order structure. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):799–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Carlson J. O., Pettijohn D. E. Torsional tension in the DNA double helix measured with trimethylpsoralen in living E. coli cells: analogous measurements in insect and human cells. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):773–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Klysik J., Wells R. D. Conformational flexibility of junctions between contiguous B- and Z-DNAs in supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2447–2451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the E coli gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2255–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternglanz R., DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y., Becherer K., Zumstein L., Wang J. C. Mutations in the gene coding for Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I affect transcription and transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2747–2751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Jackson S., Tjian R., Echols H. DNA looping between sites for transcriptional activation: self-association of DNA-bound Sp1. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):820–826. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F. Protein-DNA interactions and nuclease-sensitive regions determine nucleosome positions on yeast plasmid chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):177–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Simpson R. T. Local protein-DNA interactions may determine nucleosome positions on yeast plasmids. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):250–252. doi: 10.1038/315250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao Y. P., Wu H. Y., Liu L. F. Transcription-driven supercoiling of DNA: direct biochemical evidence from in vitro studies. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90989-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J. C., Sasker M., Stunnenberg H. G. Promoter melting by a stage-specific vaccinia virus transcription factor is independent of the presence of RNA polymerase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90412-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley M. E., Patient R. K. Highly efficient beta globin transcription in the absence of both a viral enhancer and erythroid factors. Development. 1987 Dec;101(4):815–827. doi: 10.1242/dev.101.4.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig B., Dorbic T., Rich A. The level of Z-DNA in metabolically active, permeabilized mammalian cell nuclei is regulated by torsional strain. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):755–764. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Burgi E. On the structure of the folded chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):127–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. Y., Shyy S. H., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. Transcription generates positively and negatively supercoiled domains in the template. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Laskey R. A., Finch J., Gurdon J. B. Selective DNA conservation and chromatin assembly after injection of SV40 DNA into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 May;64(1):178–188. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]