Figure 1. Experimental design.
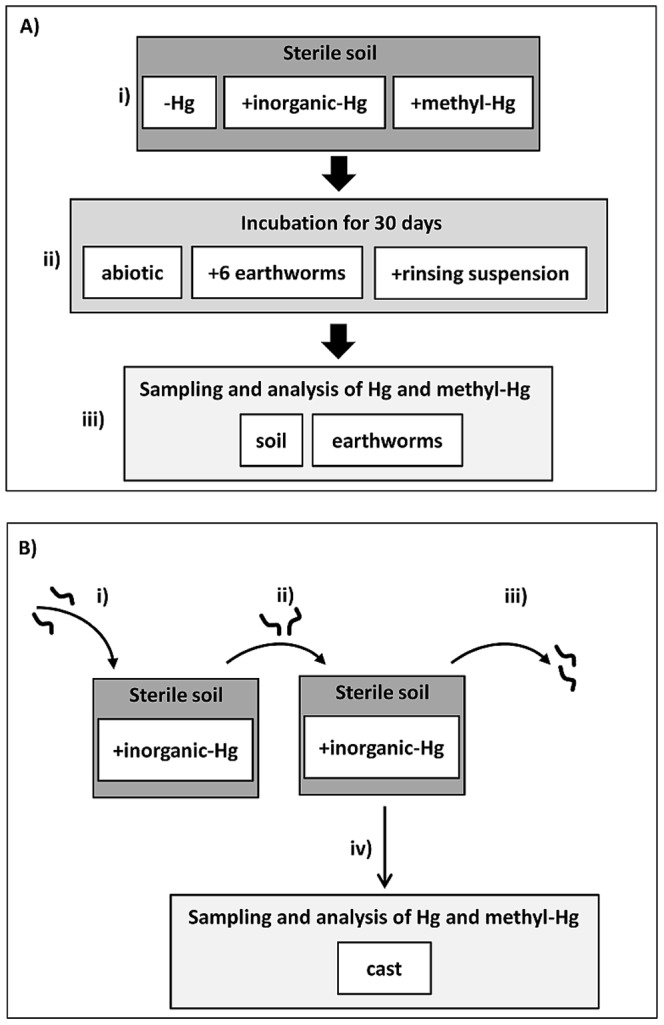
Two experimental assays (A and B) were performed: In the main experiment (A) sterile soil was either treated with inorganic Hg (+inorganic−Hg), methyl-Hg (+methyl−Hg) or without Hg (−Hg) (i). The soils were incubated abiotically, with earthworms or with a earthworm rinsing suspension for 30 days in the dark at 15°C (ii). At the end of incubation, the earthworms were removed from the soil and the Hg and methyl-Hg concentrations in the soil and earthworms were determined (iii). In a separate experiment (B), casts (excreted feces) were used as controls to study a possible methylation of Hg by organisms introduced into the soil by earthworms. Earthworms were incubated for one week in soils treated with inorganic-Hg (i) before they were placed into new boxes containing soils treated with Hg (ii). After three days, the earthworms were removed (iii). Immediately after removing the earthworms a cast sampling period has been started for 28 days (iv).
