FIGURE 6. CpG renders tBregs stimulatory by up regulating 4-1BBL on tBregs.
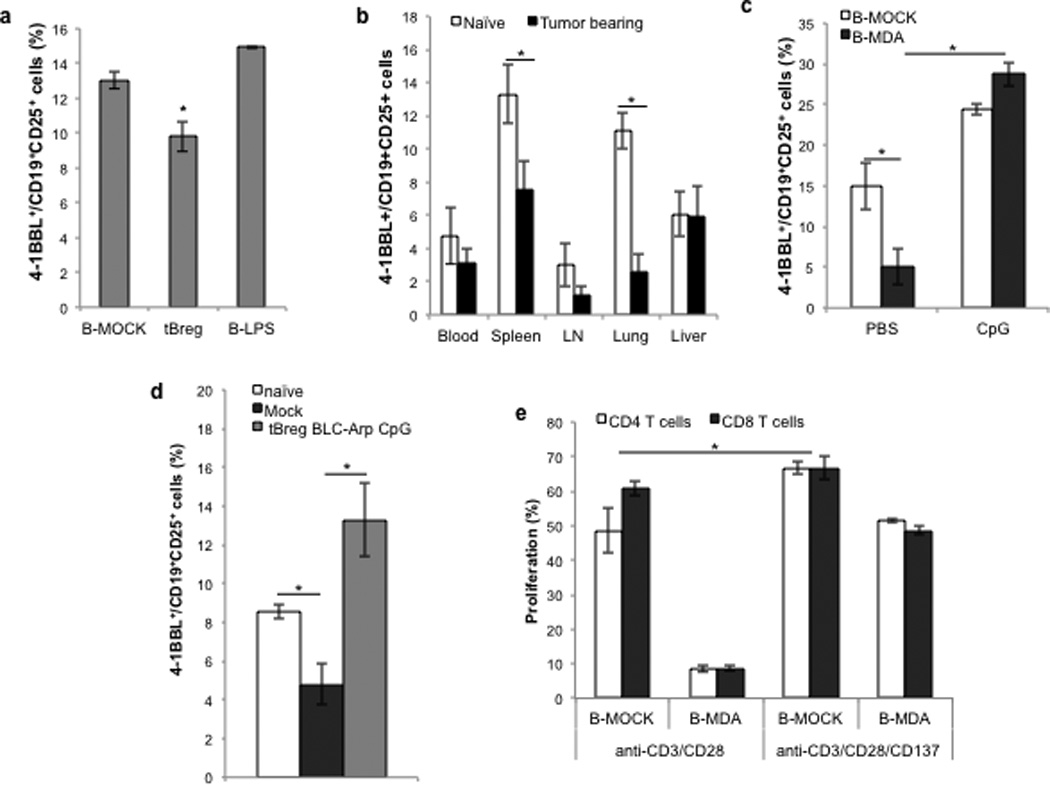
Compared with LPS-stimulated B cells (B-LPS), ex vivo-generated murine tBregs reduce surface expression of 4-1BBL (A). Shown is % ± SEM of 4-1BBL+ within CD25+ CD19+ B cells (B) of a triplicate experiment. (B) Compared with naïve mice, 4T1.2 cancer-bearing BALB/c mice have less B cells expressing 4-1BBL. Shown is % ± SEM (4 mice/group) of 4-1BBL+ within CD25+ CD19+ B cells in blood, spleen, draining lymph nodes (LN), lungs and liver. The low levels of 4-1BBL on ex vivo generated human (B-MDA, C) and murine tBregs from mice with 4T1.2 cancer (D) were drastically reversed by in vitro (C) and in vivo (D) BLC-arp/CpG treatment, respectively. The suppressive activity of tBregs was blocked in the presence of agonistic anti-4-1BB (CD137) Ab that presumably supplemented the missing 4-1BBL signaling to T cells (E). All data shown here were from triplicate experiments reproduced at least three times.
