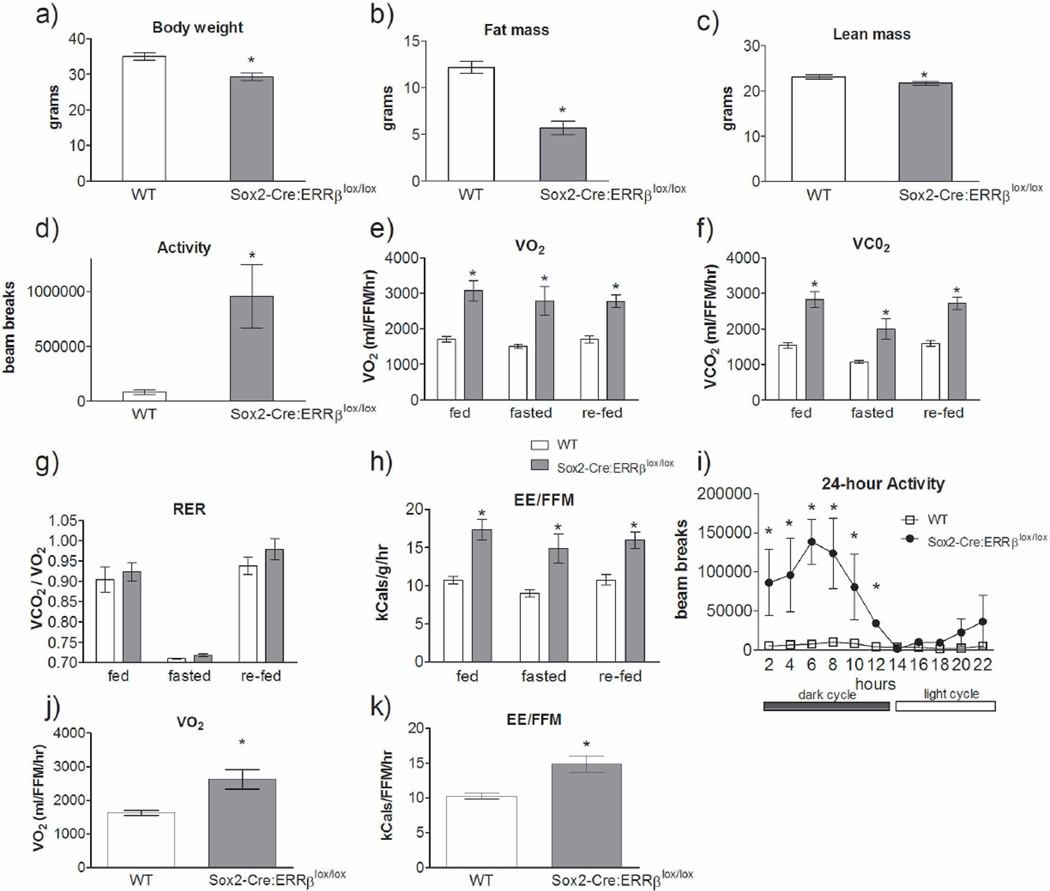
Figure 1.
Whole-body deletion of ERRβ altered systemic energy balance. Sox2-Cre:ERRβlox/lox mice have decreased a) body weight, b) fat mass and c) lean mass relative to wild-type (WT) mice. d) Physical activity levels, e) VO2 and f) VCO2 are increased, with no change in g) respiratory exchange ratio (RER), and an increase in h) whole-body energy expenditure in Sox2-Cre:ERRβlox/lox mice relative to WT. i) Physical activity over 22-hour period of time presented in 2-hour blocks [repeated measures ANOVA, fisher post-hoc: F1,16=16.82, P<0.05]. j–k) Measurements for whole-body metabolism for blocks 14 and 16, which coincided with 4–8 hours after the light cycle began. Sox2-Cre:ERRβlox/lox mice exhibited increased j) VO2 and k) energy expenditure, relative to WT mice. Data shown are mean ± SEM for each group (n=4–6/genotype). * Denotes significant difference, p<0.05.