Figure 3.
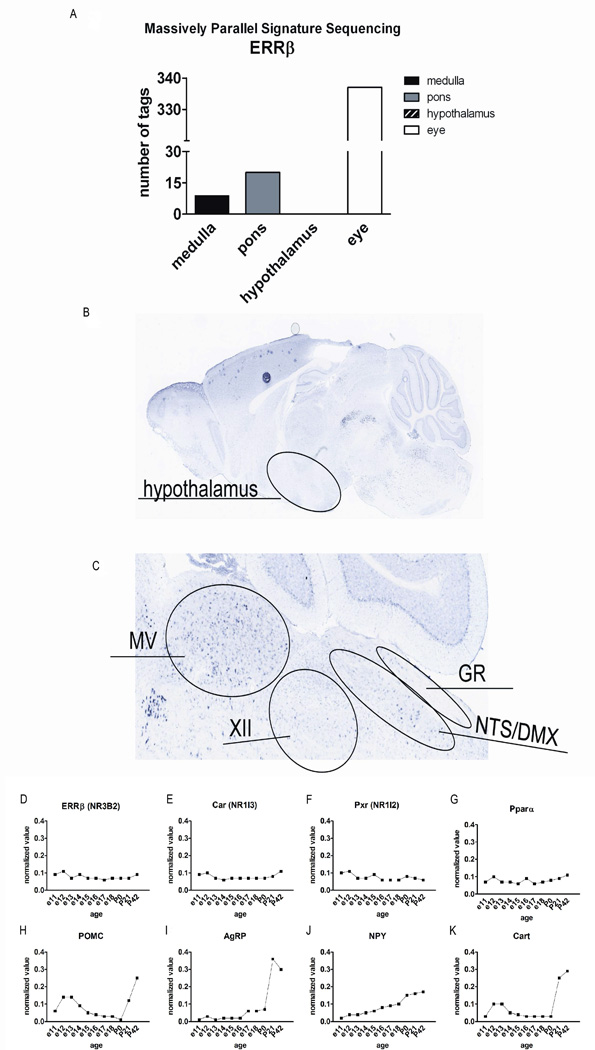
Expression analysis for ERRβ in the brain. a) Massively parallel signature sequencing expression data from mouse nervous system reveals that ERRβ is enriched in eye and hindbrain, but absent from hypothalamus. Data is obtained from GEO reference series GSE1581. b) ERRβ gene expression is primarily located in the hindbrain, and not in the hypothalamus (image credit: Allen Institute for Brain Science). c) Hindbrain ERRβ gene expression is present in the nuclei known to modulate food intake, the dorsal vagal complex (NTS/DMX), as well as other hindbrain nuclei (image credit: Allen Institute for Brain Science). d–k) Developmental microarray analysis of the hypothalamus, from embryonic day (e) 11 until postnatal day (P) 42. d) ERRβ gene expression is not present in the hypothalamus during development or in the adult. The results were confirmed by comparing gene expression levels to genes identified to have no expression in the CNS, e) Car (NR1I3) and f) Pxr (NR1I2), or in the hypothalamus, g) Pparα. h-k) Positive controls for genes known to be expressed in the hypothalamus.
