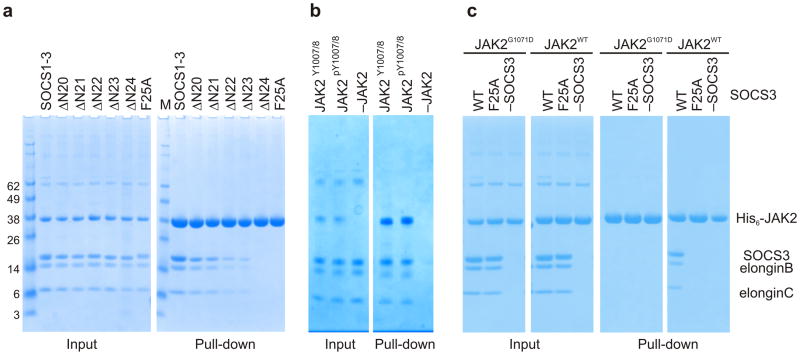
Figure 4. The KIR is required for JAK binding.
(a) Co-precipitation experiments show that SOCS3 binds JAKJH1 provided the kinase inhibitory region is intact. Lanes 2–6 show there is a gradual loss of binding as the N-terminal residues of the SOCS3 KIR are removed, as well as when Phe25 is mutated to Alanine. The SOCS1-SOCS3 chimera is shown as a positive control (b) Co-precipitation experiments show that SOCS3binds activated (pY1007/8) and dephosphorylated (Y1007/8) JAK2JH1 with similar affinity. Dephosphorylated JAK2JH1 was prepared by co-expressing it with the phosphatase PTP1B and then used in co-precipitation experiments with SOCS3 as described in panel a. A western blot of this experiment probed with a pY1007/8 specific antibody shows that JAK2 co-expressed with PTB1B was >95% dephosphorylated (Supplemental Figure 5) (c) Co-precipitation experiments show that SOCS3 does not bind JAK2JH1 if the JAK2 GQM motif is mutated (G1071D). SOCS3F25A is shown as a negative control.