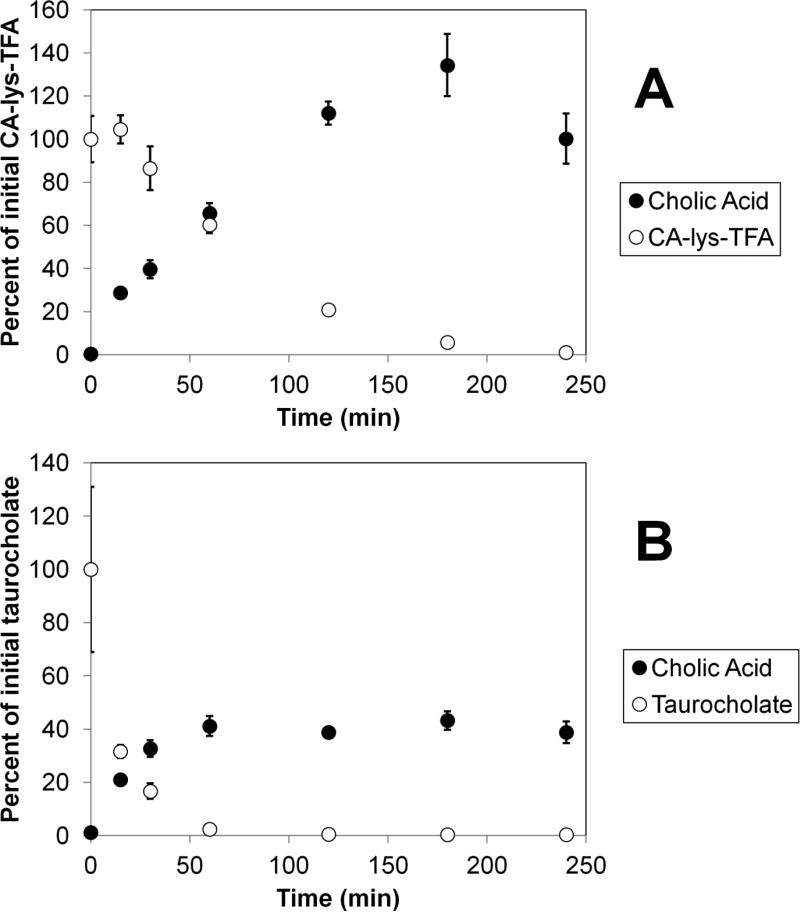
Figure 5.
Comparative stabilities of CA-lys-TFA and taurocholate against choloylglycine hydrolase from Clostridium perfringens. Panel A shows the loss of CA-lys-TFA (initially 2 mM) and the corresponding appearance of deconjugated cholic acid. Panel B shows the loss of taurocholate (initially 2 mM) and the corresponding appearance of deconjugated cholic acid. Each study was performed in triplicate. After 1 h, only 2.4% of taurocholate remained, while 60.4% of CA-lys-TFA remained, suggesting improved stability of the amide bond linking trifluoroacetyl lysine to cholic acid, compared to the natural amino acid conjugate.