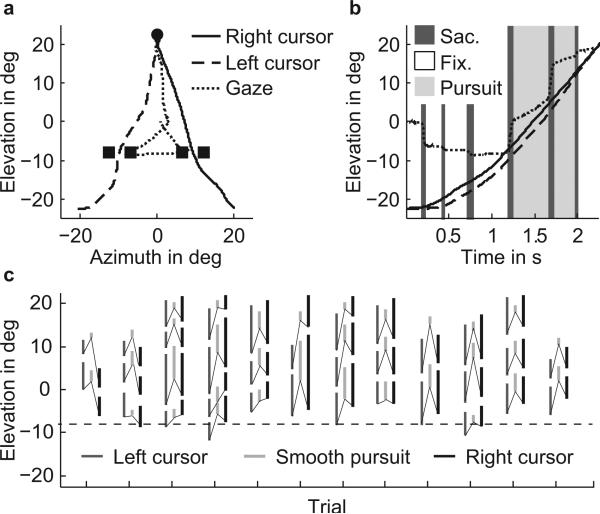
Figure 3.
(a) Left cursor (dashed line), right cursor (solid line) and gaze (dotted line) paths for a single trial (S2, scene 8, experiment 1). The goal and gates are represented by the circle and squares, respectively. (b) Corresponding time traces in the elevation direction for gaze (dotted line), left cursor (dashed line) and right cursor (solid line). Shaded areas indicate either fixations (white), saccades (dark gray) or smooth pursuit (light gray). (c) Elevation position of smooth pursuit paths for trials of scene 8, experiment 1, shown as light gray lines (S2). The dark gray and black lines show the elevation position of the left and right cursor, respectively, in the same time frame as the corresponding smooth eye movement (light gray bar). For clarity. The thin lines connect position of pursuit at onset of pursuit with the corresponding position of the left and right cursor at that onset time. The dashed line indicates the elevation position of the gates.