Figure 2. Strong loss of function mutant pqn-47(tm2707) terminally arrests during the L1 molt.
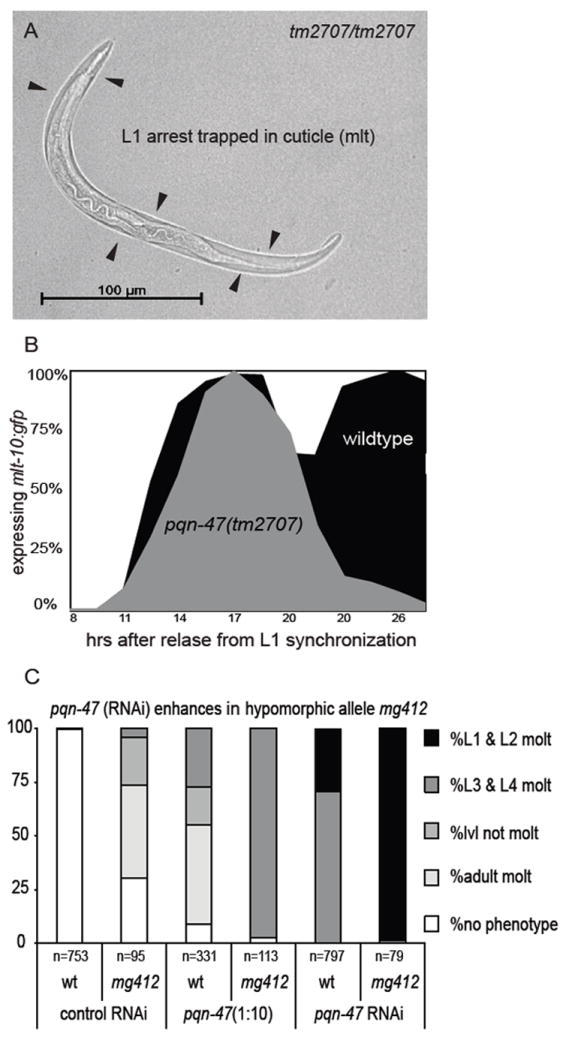
(A) at 48 hours, a tm2707 homozygote arrested in the L1 molt (by absence of rescuing transgene). (B) tm2707 homozygous animals recover from L1 starvation and enter into the first larval molt with apparently normal kinetics as reflected by their expression of the molting reporter mlt-10p∷gfp-pest. However, unlike wildtype animals that quickly finish the molt and turn mlt-10p∷gfp-pest off as L2s, only to then repeat the molting cycle, tm2707 homozygotes initiate but are unable to complete the L1 molt, remain trapped in the cuticle and turn off mlt-10p∷gfp-pest. Time course at 25°C post synchronization, wild type n>190 and tm2707 n>80 (C) pqn-47 (RNAi) recapitulates the phenotypes of strong and weak loss of function alleles of pqn-47 as well as enhancing the hypomorphic allele mg412. Synchronized L1s were plated on to RNAi plates and grown at 25°C for 66 hrs. Gravid adults expressing mlt-10p∷gfp-pest or animals in a supernumerary molt were scored as adult molt.
